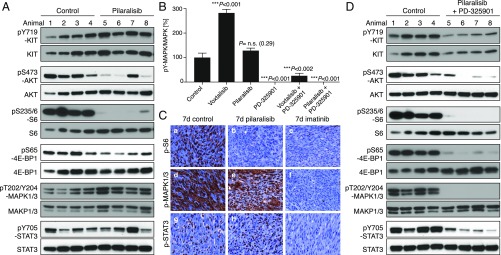
Fig. 5.
Inhibition of PI3K resulted in a significant reduction in GIST proliferation. KitV558Δ/+ mice (n = 4/group) were treated for 4 h (A) with pilaralisib (100 mg/kg) alone, (B) with PD-325901 (15 mg/kg) alone, and (D) with both pilaralisib (100 mg/kg) and PD-325901 (15 mg/kg) and analyzed by immunoblotting. (B) Comparison of the level of activation of phospho-MAPK1/3 in GIST from mice treated with voxtalisib and pilaralisib alone or in combination with PD-325901. The level of activation of phospho-MAPK1/3 was determined by densitometry analysis of the respective bands from Western blots and measured as the ratio of phospho/total for each protein compared with control. The scale is arbitrary units (intensity of gray shading). (C) Representative results of IHC analysis of GIST after long-term (7 d) treatment of KitV558Δ/+ mice with vehicle (control), pilaralisib, or imatinib. As a positive control for IHC, imatinib down-regulated all three signaling readouts—p-MAPK, pS6, and p-STAT3—as reported previously (11). Antibodies used are specific for pS6 (a–c), p-MAPK1/3 (d–f), and p-STAT3 (g–i) on 5-µm sections of GISTs. Tumor sections from the different treatment groups (n ≥3 animals each) were placed next to each other on the same microscope slide to enable cross-comparison of staining intensities (40× objective).