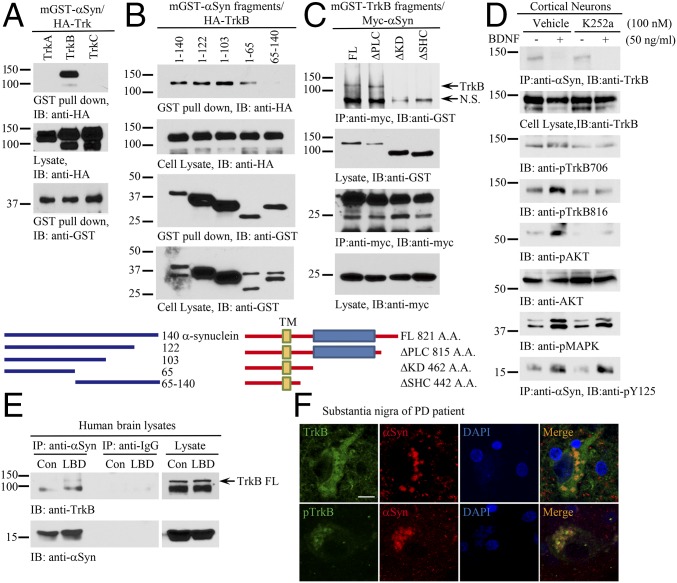
Fig. 1.
α-Synuclein selectively interacts with TrkB receptors. (A) α-Syn specifically interacts with TrkB receptors. GST pull-down assay was conducted from HEK293 cells cotransfected with mammalian GST–α-Syn and HA-Trks. (B) α-Syn N terminus is implicated in binding TrkB. Different mGST-tagged α-Syn truncated were cotransfected with HA-TrkB into HEK293 cells. A GST pull-down assay was performed, and coprecipitated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-HA (Top). Schematic diagram of α-Syn truncations (Bottom). (C) TrkB kinase domain is indispensable for α-Syn to interact with TrkB. (Top) Mapping assay for TrkB ICD required for binding to α-Syn. (Bottom) Schematic diagram of TrkB domains. (D) BDNF inhibits α-Syn/TrkB association. Cortical neurons were pretreated with K252a (100 nM) for 15 min, followed by BDNF treatment (50 ng/mL) for 30 min. Coimmunoprecipitation was performed with anti–α-Syn, and the coprecipitated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-TrkB (Top). Cell lysates were probed with various antibodies (second through bottom panels). (E) α-Syn associates with TrkB in LBD human patient brains. Brain lysates from LBD patients were immunoprecipitated with control IgG or anti–α-Syn, and the coprecipitated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-TrkB. (F) TrkB colocalizes with α-Syn in the LBs of PD patients. Immunofluorescent costainings with anti-TrkB or p-TrkB 706 (Green) and α-Syn (Red) were conducted with human PD brain sections. The nuclei were stained with DAPI. (Scale bar, 20 μm.)