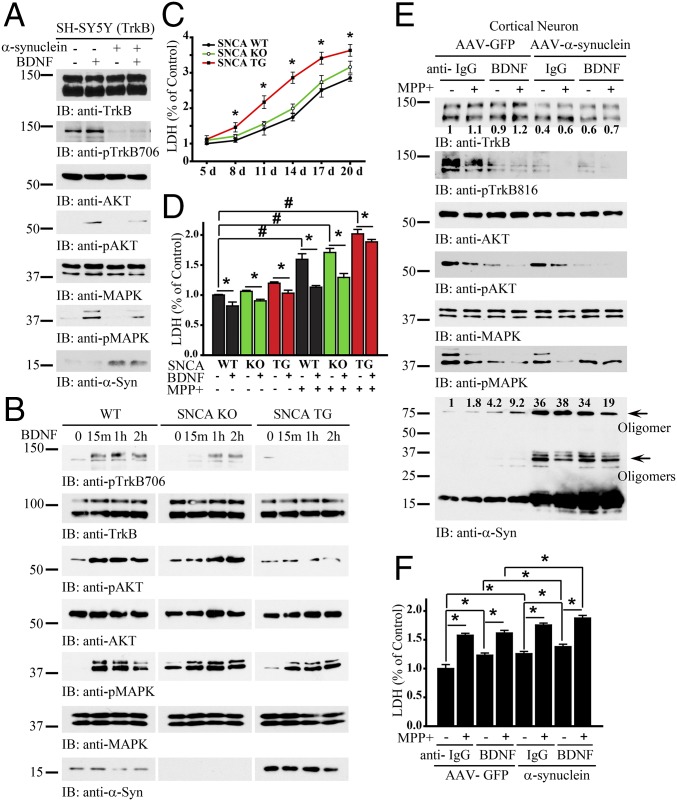
Fig. 2.
Overexpression of α-Syn blocks BDNF/TrkB signaling. (A) α-Syn inhibits BDNF/TrkB signaling. TrkB stably transfected SH-SY5Y (BR6) cells were transfected with α-Syn, followed by treatment with BDNF for 10 min. p-TrkB and its downstream effectors, p-Akt and p-MAPK, were analyzed in the cell lysates. (B) BDNF/TrkB signaling is blocked in SNCA overexpressing transgenic neurons. Wild-type, SNCA KO, and SNCA transgenic neurons were treated with BDNF for 15 min, 1 h, or 2 h, and the pTrkB signaling cascade was probed with various antibodies. (C) LDH assay of SNCA transgenic, SNCA KO, and wild-type dopaminergic neurons. (D) α-Syn overexpression decreases the neuroprotective effects of BDNF against MPP+-induced neuronal cell death. MPP+ sensitized α-Syn–induced neuronal cell death. Shown are SNCA transgenic, SNCA KO, or wild-type dopaminergic neurons in the presence or absence of BDNF, treated with MPP+ (200 μM) or not for 24 h. LDH assay was conducted with cell medium. (E and F) Overexpression of α-Syn decreases TrkB levels and elevates neuronal cell death. Primary cortical cultures were infected with AAV virus expressing α-Syn or GFP control, followed by treatment with anti-BDNF or anti-IgG, then treated with MPP+ (200 μM) for 24 h. Immunoblotting analysis of cell lysates with various antibodies (E) and LDH assay of the treated cells (F). Data are shown as mean + SEM. n = 3 each group. *P < 0.05, #P < 0.01. The relative intensities of the band that were quantified with Image J were indicated in the immunoblots.