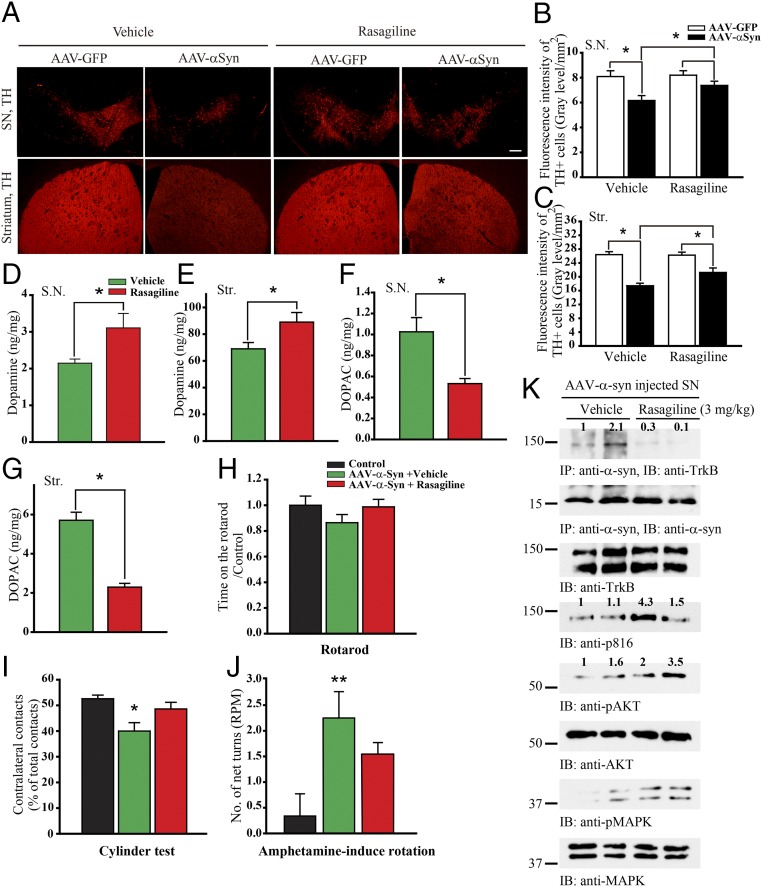
Fig. 5.
Rasagiline disrupts α-Syn/TrkB complex and rescues dopaminergic neurons from α-Syn–induced cell death. (A) Rasagiline reduces TH loss induced by α-Syn. C57BL/6 mice were injected with AAV-GFP or AAV–α-Syn into the left and right SN, respectively, followed by rasagiline (3 mg·kg·d) treatment for 10 d. TH expression in SN and striatum was analyzed by immunofluorescent staining. (Scale bar, 200 μm.) (B and C) Quantification of TH-positive fluorescent signaling in SN (B) and striatum (Str) (C). Data are shown as mean + SEM. n = 6 sections each group. *P < 0.05. (D and E) DA concentrations in SN and striatum were increased by rasagiline in α-Syn–overexpressed mice. (F and G) DA metabolite DOPAC concentrations in SN and striatum were decreased by MAO-B inhibitor, rasagiline, in α-Syn–overexpressed mice. Data are shown as mean + SEM. n = 3 each group. *P < 0.05. (H–J) Motor behavioral assays. Overexpression of α-Syn induced motor impairment, and rasagiline significantly improved the motor functions. Data are shown as mean + SEM. n = 8 each group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (K) Rasagiline disrupts α-Syn/TrkB complex and restores p-TrkB signaling. Coimmunoprecipitation assay with anti–α-Syn from SN tissues treated with or without rasagiline and coprecipitated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting. SN lysates were probed by various indicated antibodies.