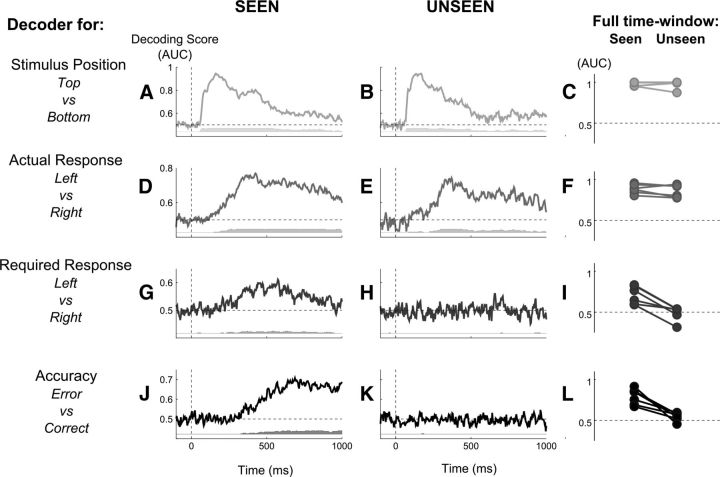
Figure 2.
Decoding perception, action, intention, and accuracy, for conscious and nonconscious trials. Multivariate decoding was applied either to each time sample (central columns) or to the full trial time window (right columns). Results demonstrate that while stimulus position and actual response could be decoded in both conscious and nonconditions with high accuracy, the required response and the accuracy could be decoded solely in conscious conditions. A, B, D, E, G, H, J, K, Central columns, AUC, a measure of decoding accuracy, is plotted after averaging across subjects, aligned on stimulus onset, separately for the stimulus position decoder (top vs bottom, A, B), actual response decoder (left vs right, D, E), required response decoder (left vs right, G, H), and accuracy decoder (error vs correct, J, K), respectively, in seen (A, C, E, G) and unseen (B, D, F, H) conditions. Gray bars below each graph indicate, for each time point, the number of subjects presenting an above-chance classification score at that instant as computed by cluster analysis. C, F, I, L, Right column, For all six subjects, change in classification scores (AUC) between seen (left points) and unseen (right points) conditions are plotted separately for the stimulus position decoder (C), actual response decoder (F), required response decoder (I), and accuracy decoder (L). In each case, decoding was applied on all the sensors and time points from the full trial time window (0–800 ms after stimulus presentation).