Figure 5.
The R927 Residue Adjacent to Four Polymorphic Sites Keeps Sw-5b in an Autoinhibited State.
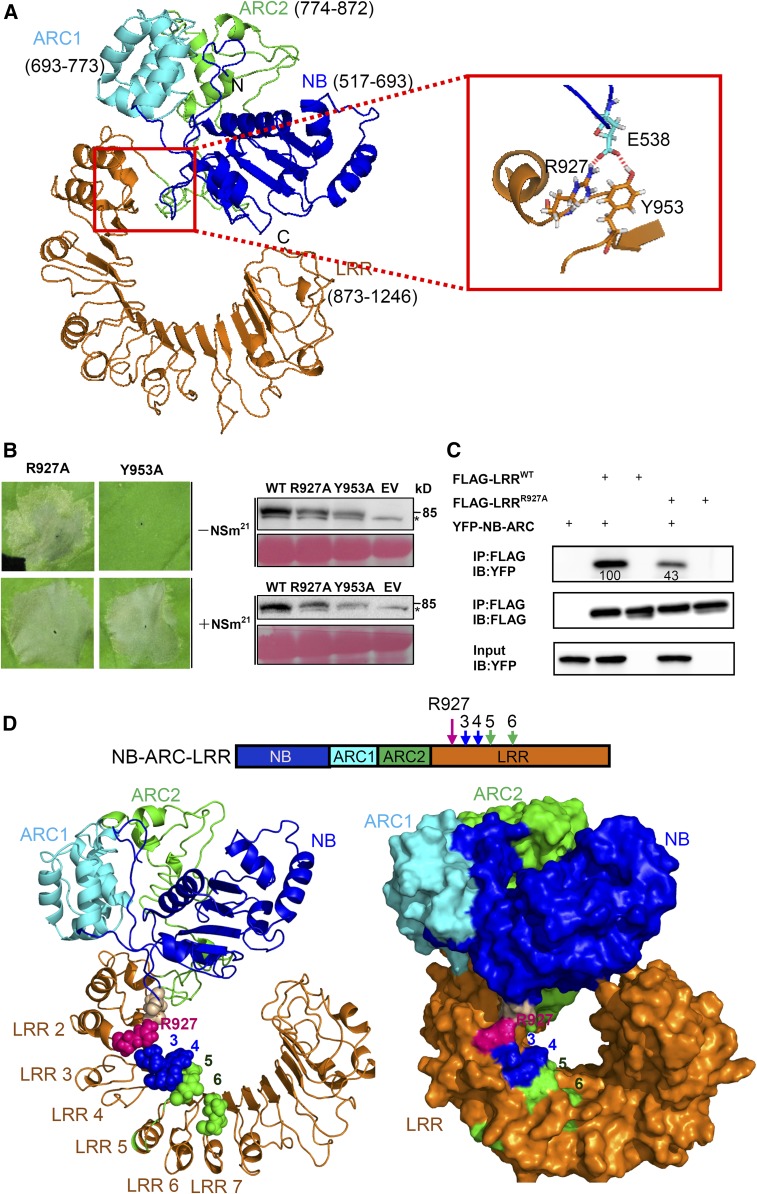
(A) Putative interaction interface between the LRR and NB-ARC domain on the three-dimensional homology structure of Sw-5b NB-ARC-LRR is shown in the red box. NB (blue), ARC1 (cyan), ARC2 (green), LRR (amino acid residue 873–1246; orange) are subdomains of Sw-5b NB-ARC-LRR. The enlarged red boxed on the right shows that amino acid R927 and Y953 in the LRR and E538 in the NB can form a putative contact site.
(B) The R927A (YFP-NB-ARC-LRRR927) but not the Y953A (YFP-NB-ARC-LRRY953) mutant results in cell death in the absence of NSm21 in leaves of N. benthamiana plants. Expression of R927A and Y953A induces cell death in the presence of NSm21. The right panels show the accumulation of proteins using an anti-YFP antibody. The sizes of proteins in kilodaltons are shown to the right of the blot. Asterisk represents the nonspecific band. Ponceau S staining was used to show protein loading.
(C) The effect of the R927A mutant on the physical interaction between the LRR and NB-ARC domains. Wild-type Sw-5b LRR fused to FLAG tag (FLAG-LRRWT) or R927A mutant (FLAG-LRRR927A) was used to immunoprecipitate YFP-NB-ARC. The amount of YFP-NB-ARC precipitated by the wild type or R927A was quantified by ImageQuant software. IP, immunoprecipitation with specific antibody; IB, immunoblot with specific antibody.
(D) Location of R927 residue and the polymorphic sites 3, 4, 5, and 6 on the three-dimensional homology structure of Sw-5b NB-ARC-LRR. The upper panel shows NB-ARC-LRR with the indicated position of the R927 residue and the four polymorphic sites. The ribbon and surface homology structure model of Sw-5b NB-ARC-LRR are shown in the left and right, respectively. The R927 residue is shown in a purple sphere, while the four polymorphic sites are shown as in Figure 4E.