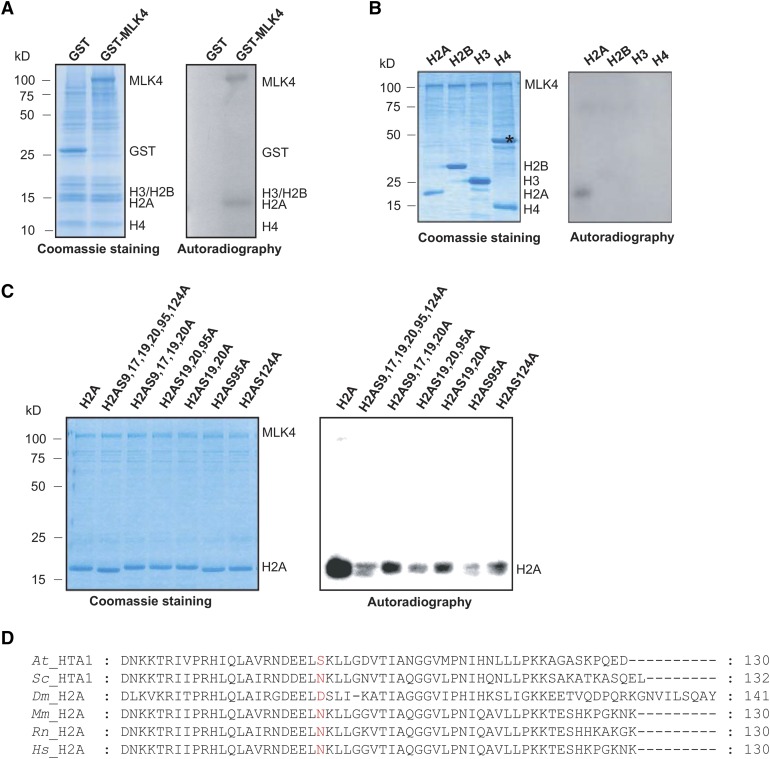
Figure 2.
Phosphorylation of H2A at Serine 95 by MLK4.
(A) The kinase activity of MLK4 on cauliflower core histones was assessed. The GST-MLK4 purified from E. coli incubated with cauliflower core histone to test in vitro phosphorylation activity. The positions of H2A, H2B, H3, H4, MLK4, and GST alone are indicated.
(B) MLK4 phosphorylates H2A. The ability of MLK4 to phosphorylate H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 was assessed. Asterisk indicates a nonspecific band.
(C) The activity and specificity of the MLK4 kinase were assessed using different substrates. The substrates were H2A fused with His and were either wild-type H2A or had serine-to-alanine substitutions at various residues.
For (A) to (C), the left panel shows the Coomassie blue-stained gel, and the positions of the different histones and MLK4 are indicated on the right. Autoradiography (right panel) shows kinase activity and specificity. Molecular mass markers in kilodaltons are indicated on the left.
(D) Alignment of histone H2A proteins from Arabidopsis, yeast (S. cerevisiae), fruit fly (Drosophila), mouse (Mus musculus), Rat (Rattus norvegicus), and human (Homo sapiens). The serine 95 of Arabidopsis H2A and corresponding sites from different species are marked in red. The sequences of H2As were aligned using ClustalW and examined with MEGA5.