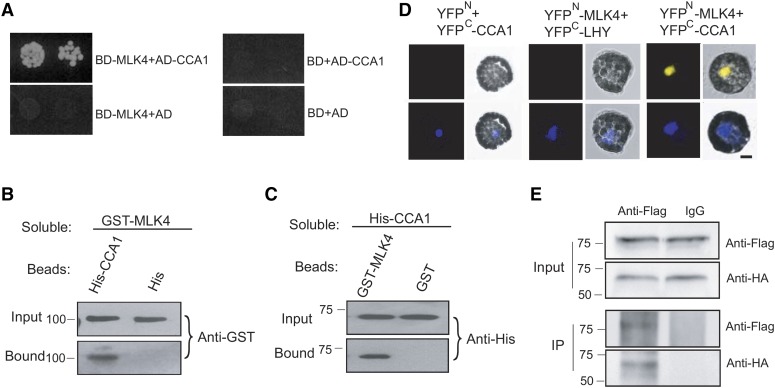
Figure 4.
MLK4 Interacts with CCA1.
(A) A yeast two-hybrid assay revealed an interaction between MLK4 and CCA1. The growth of two dilutions (2 × 10−2 and 2 × 10−3) of the yeast culture on SD medium lacking Trp, Leu, His, and adenine is shown.
(B) Beads containing a His tag (His) or His-fused CCA1 were assayed for their ability to bind to soluble GST-fused MLK4. The input and bound proteins were detected with an antibody to GST (anti-GST).
(C) Beads containing a GST tag or GST-fused MLK4 were assessed for their ability to bind to soluble His-fused CCA1 and detected with antibody to His (anti-His).
(D) Either MLK4 fused to the N terminus of YFP or the N terminus of YFP alone were tested for their ability to bind to the C terminus of YFP fused to LATE ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL (LHY) or the C terminus of YFP fused to CCA1. Yellow fluorescence and a bright-field image were recorded and the resulting images were merged. Twenty-five cells were examined for each transformation. Bar = 10 µm.
(E) Coimmunoprecipitation of MLK4 and CCA1. FLAG-CCA1 and HA-MLK4 were cotransformed into Arabidopsis protoplasts, and the expressed proteins were immunoprecipitated using an anti-FLAG antibody and detected with anti-Flag and anti-HA.
In (A) to (E), experiments were repeated at least three times, and representative experiments are shown. In (B) to (E), molecular mass markers in kilodaltons are indicated on the left; the sizes of the bands are as expected.