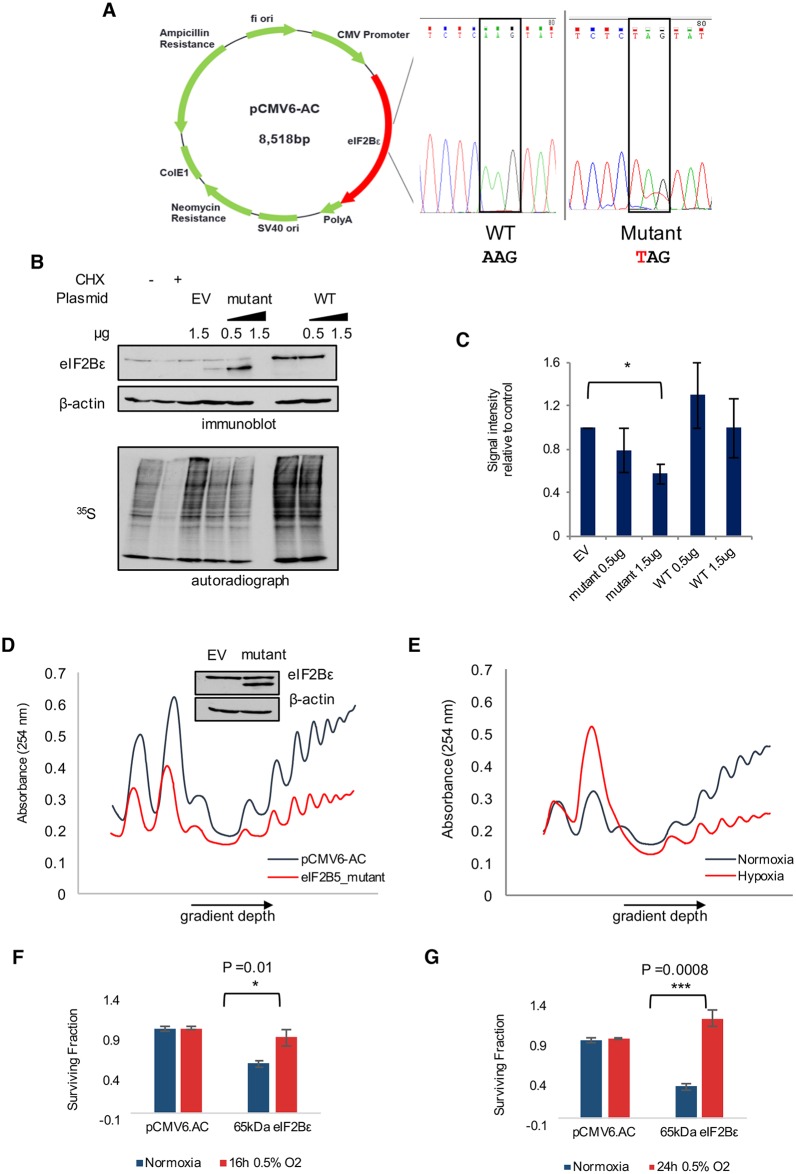
Fig 7. Expression of a 65kDa isoform of eIF2Bε leads to a global decrease in protein synthesis.
(A) Site-directed mutagenesis was used to introduce a stop codon into EIF2B5 (within 1 codon of where intron retention introduces an early stop). (B) Expression of full-length (wild-type [WT]) or mutated eIF2Bε (mutant) was performed for 24 h in SQ20B cells (upper), followed by pulse-labeling with 35S methionine/cysteine (lower) to measure changes in protein synthesis compared to expression of an empty vector pCMV6-AC (EV). Cells treated with cyclohexamide (CHX) were used as a control for inhibition of translation initiation. (C) Image quantification of total 35S signal from autoradiographs of 4 independently conducted experiments. Data collected from n = 4 independently conducted experiments, *P < 0.01 (Student t test). (D) Polysome profile depicts SQ20B cells expressing the 65kDa isoform of eIF2Bε for 36 h compared to cells expressing control pCMV6-AC, with supporting immunoblot shown above. (E) Polysome profiling of hypoxic versus normoxic SQ20B cells. (F) Clonogenic assay of SQ20B cells expressing control plasmid (pCMV6.AC) or 65kDa eIF2Bε in normal oxygen or 0.5% O2 for 16 h. Analysis of 3 biological replicates quantified to right (P value reported for Student t test). (G) Clonogenic assay of SQ20B cells expressing control plasmid (pCMV6.AC) or 65kDa eIF2Bε in normal oxygen or 0.5% O2 for 24 h. Analysis of 3 biological replicates quantified to right (P value reported for Student t test). Additional data used to create this figure are included in S1 Data.