Figure 4. Activation of ERK pathways within neutrophils are required for PAO1-induced neutrophil trans-epithelial migration.
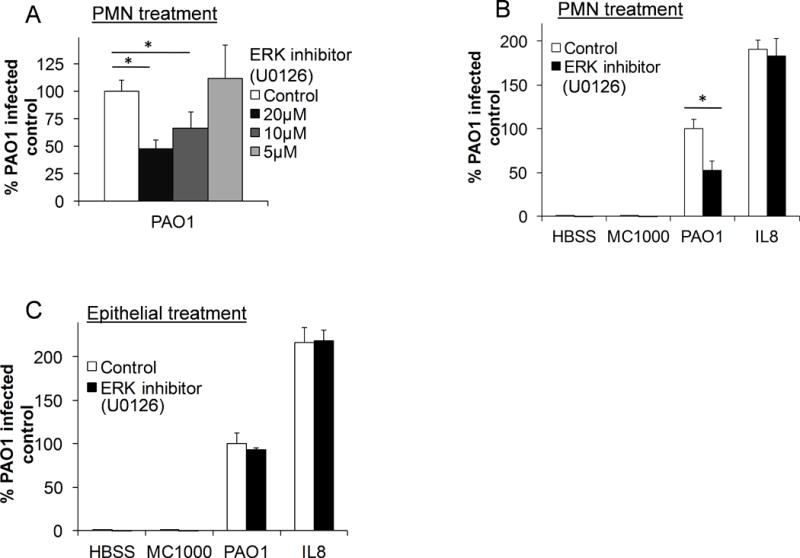
A) Healthy primary human neutrophils were pre-treated for 30 min. with escalating doses of the ERK inhibitor, U0126, or vehicle control (DMSO 1:1000) prior to migration across untreated H292 monolayers infected with PAO1. B) Neutrophils were pretreated for 30 min. with U0126 (20μM) or vehicle control (DMSO 1:1000) and allowed to migrate across an H292 monolayer infected with PAO1, MC1000, mock-infection (HBSS), or towards exogenous neutrophils chemoattractant, IL-8. C) H292 monolayers were pretreated with U0126 (20μM) or vehicle control (DMSO 1:1000) prior to infection with PAO1, MC1000 or mock-infection (HBSS). Untreated neutrophils migrated across the pretreated epithelium in response to infection, or towards exogenous IL-8. For all experiments, relative neutrophil migration into the apical compartment was assessed after 2h by total myeloperoxidase activity. Migration was corrected for using standard curves generated for each drug treatment of neutrophil. Data are shown as mean corrected value +/− standard deviation. Experiments were performed on at least 3 occasions with n≥3 technical replicates. P values were calculated by ANOVA with Dunnett’s test (A) or paired Student’s t-test (B, C). P values ≤0.05 was consider significant.
