Figure 5. WT zebrafish adult tissue types expression of zebrafish eCBs genes.
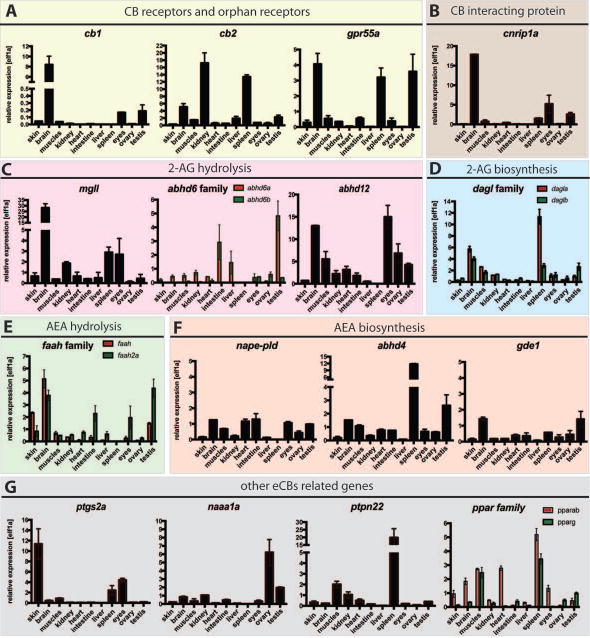
qPCR detection of zebrafish eCBs genes in zebrafish tissues (X axis: skin, brain, muscles, kidney, heart, intestine, liver, spleen, eyes, ovary, testis) using primers against (A) Cannabinoid Receptors, cb1 and cb2 and putative orphan receptor gpr55a (B) cannabinoid receptor interacting proteins, cnrip1a, (C) enzymes responsible for 2-AG hydrolysis mgll, abhd6a and abhd6b and abhd12, (D) enzymes responsible for 2-AG synthesis, dagla and daglb, (E) enzymes responsible for AEA hydrolysis faah and faah2a (F) enzymes responsible for AEA synthesis nape-pld, abhd4 and gde1 (G) genes associated with the eCBs, ptgs2A, naaa1a (asah1a), ptpn22, pparab and pparg. Elf1α was used as internal control to determine the relative mRNA expression. Relative average expression ± SEM (qPCR results are representative of two experimental repeats and 2 repeats/experiment). GraphPad Prism 7 software was used for statistical analysis.
