Fig. 9.
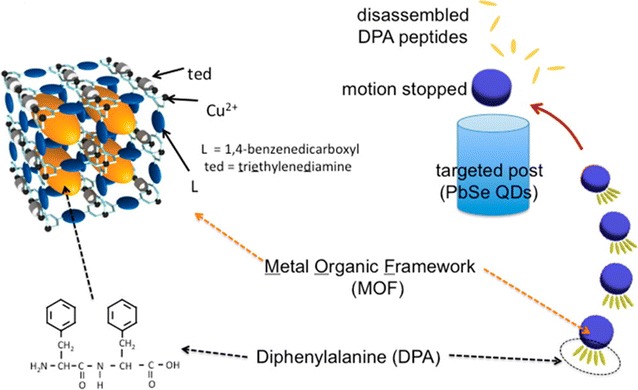
Scheme depicting peptide-MOF motor swimming toward high pH. The reassembly of released hydrophobic DPA peptides on the edges of the framework produces an asymmetric surface tension distribution that powers motion towards the higher surface tension side (left). A change of pH gradient in environment prompts completion of the motion due to higher pH conditions disassembling DPA peptides on the MOF (right)
(Reprinted (adapted) with permission from Ref. [98]. Copyright 2015 American Chemical Society)
