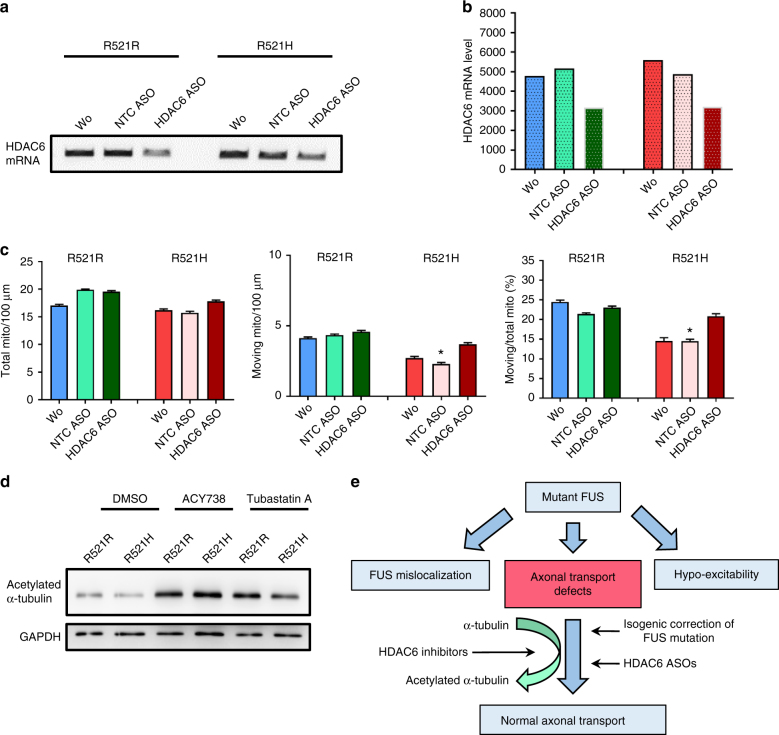
Fig. 6.
Effect of genetic HDAC6 knockdown and increased acetylation levels of α-tubulin by HDAC6 inhibition. a RT-PCR validation of knockdown by an antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) against HDAC6 in MNs. b Quantification of the RT-PCR results of the gel shown in a illustrating the HDAC6 knockdown by the ASO. c Knockdown of HDAC6 using an ASO in patient-derived MNs increased axonal transport based on tracking mitochondrial movement (total number, moving number, and ratio between total and moving mitochondria). Scrambled ASO was used as a negative control (NTC ASO). n = 20, n = 19, n = 18, n = 10, n = 11, n = 10 for R521R, R521R + NTC ASO, R521R + HDAC6 ASO, R521H, R521H + NTC ASO, R521H + HDAC6 ASO, respectively; ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey’s test, *P value of 0.05. d Western blot from MNs (R521H mutant line 2/2 and isogenic control R521R), with and without treatment with ACY-738 or Tubastatin A at day 31 of differentiation. The blot was probed with antibodies directed to acetylated α-tubulin, and GAPDH. e Schematic representation of our results indicating that HDAC6 inhibition rescues axonal transport defects in FUS-iPSC-derived motor neurons through increasing acetylation levels of α-tubulin