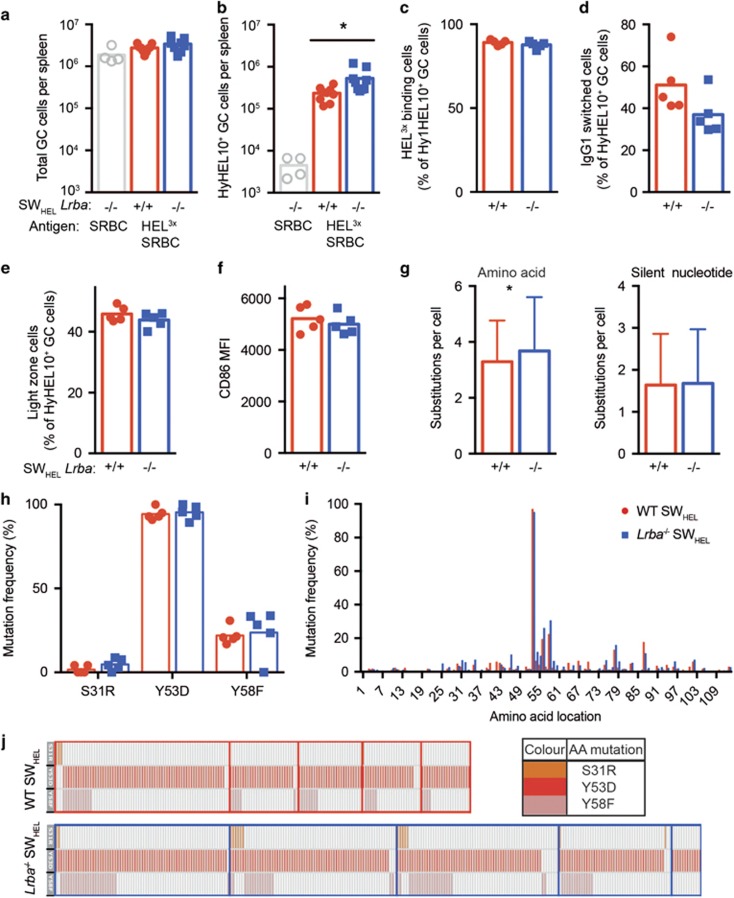
Figure 6.
Normal GC formation and affinity maturation by LRBA-deficient B cells. CD45.1 congenic C57BL/6 recipient mice, with WT LRBA, were injected intravenously with 30 000 HyHEL10+ SWHEL spleen B cells from Lrba−/− or Lrba+/+ C57BL/6 donor mice. The recipient mice were immunised two times on days 0 and 4 after B-cell transfer with HEL3X-SRBC, or unconjugated SRBC for a control group of recipients, and spleen cells were analysed by flow cytometry, sorting and single-cell Igh sequencing on day 15. (a) Total Fashi CD38− B220+ GC B cells per spleen of individual mice, and arithmetic mean for each group. (b) Donor-derived HyHEL10+ CD45.2+ CD45.1− GC B cells per spleen. (c) Affinity-matured cells, measured as % donor-derived GC B cells stained brightly with 200 ng/ml HEL3X. (d) IgG1-switched cells, measured as % of donor-derived GC B cells. (e) Light-zone CD86+ CXCR4− GC B cells, measured as % of donor-derived GC B cells. (f) CD86 MFI on donor-derived GC B cells. (g) Number of VDJH amino-acid changing or silent nucleotide substitutions per donor-derived GC B cell. (h) Percentage of donor-derived GC B cells with affinity-increasing VDJH mutations S31R, Y53D or Y58F. (i) Percentage of donor-derived GC B cells with substitutions at each VDJH amino-acid position. (j) Co-occurrence of S31R, Y53D and Y58F mutations (rows) in individual cells (columns) sorted from separate recipient mice (boxes). Data are pooled from two independent experiments with comparable results. N=9 mice per HEL3X-immunised group and four unconjugated controls. Statistical analysis was carried out using t-test: *P<0.05.