Figure 7.
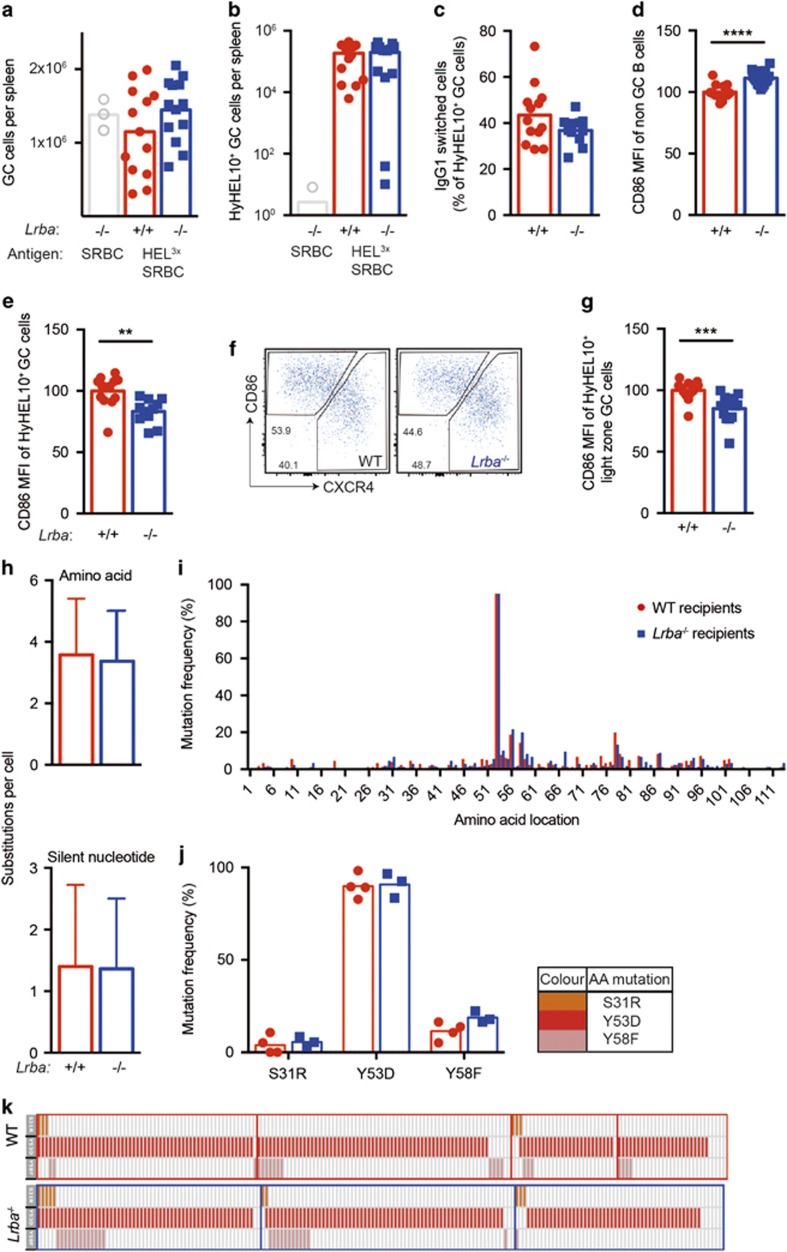
Normal GC formation and affinity maturation by LRBA WT B cells in LRBA-deficient recipients. The 30 000 HyHEL10+ SWHEL B cells from Rag1−/− CD45.1 congenic mice, with WT LRBA, were injected into the circulation of Lrba−/− (n=13, blue symbols) or Lrba+/+ (n=13, red symbols) C57BL/6 recipient mice, so that all T- and B-cell specificities other than the HyHEL10+ B cells were derived from the recipient mice. The recipient mice were immunised two times with HEL3X-SRBC on days 0 and 4 after B-cell transfer, or unconjugated SRBC for a control group of recipients, and spleen cells analysed by flow cytometry, sorting and single-cell Igh sequencing on day 15. (a) Total Fashi CD38− B220+ GC B cells per spleen of individual mice, and arithmetic mean for each group. (b) Donor-derived HyHEL10+ CD45.2− CD45.1+ GC B cells per spleen. (c) IgG1-switched cells, measured as % of donor-derived GC B cells. (d and e) Relative cell surface of CD86 MFI on (d) all B220+ B cells or (e) donor-derived GC B cells, normalised to mean of Lrba+/+ recipient group in each experiment. (f) Representative plots of donor-derived GC B cells, and gates on light-zone (LZ, CD86hi CXCR4lo) and dark-zone (CD86lo CXCR4hi) GC cells. (g) Relative cell surface CD86 MFI on LZ donor-derived GC B cells, normalised to mean of Lrba+/+ recipient group in each experiment. (h) Number of VDJH amino-acid changing or silent nucleotide substitutions per donor-derived GC B cell. (i) Percentage of donor-derived GC B cells with substitutions at each VDJH amino-acid position. (j) Percentage of donor-derived GC B cells with affinity-increasing VDJH mutations S31R, Y53D or Y58F. (k) Co-occurrence of S31R, Y53D and Y58F mutations (rows) in individual cells (columns) sorted from separate recipient mice (boxes). Data are pooled from two independent experiments with comparable results. Statistical analysis was carried out using t-test: **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.