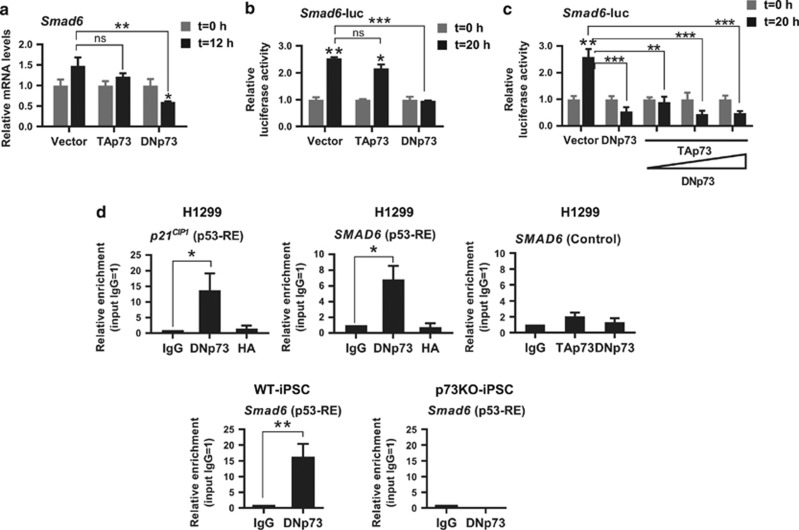
Figure 7.
Smad6 is a direct DNp73 transcriptional target. (a–c) P19 cells were transfected with either (a) TA-, DNp73 or vector control, or (b,c) Smad6-promoter reporter system. After 18 h cells were serum-deprived for 24 h and then treated with BMP4. At the indicated time points samples were collected and analyzed. (a) Quantification of Smad6 expression level was analyzed by qRT-PCR. (b and c) Transcriptional analysis was performed with the reporter vector pGL2-mSmad6-promoter (-3123)-luc, a BMP-responsive reporter construct that includes the p53-RE, together with the indicated expression vectors in the presence or absence of BMP4. (c) TAp73 (0.2 ug) was co-transfected with increasing amounts of DNp73 (0.2–0.6 μg) before BMP4 treatment. Luciferase activity was normalized by the Renilla activity of the same lysate. Bars represent mean values±S.E.M of at least four experiments; ns: not significant. (d) ChIP analysis of H1299 cells cultured in 10% serum conditions were performed using isotypic-antibody (rabbit IgG), anti-HA or anti-DNp73 specific antibodies. Real-time PCR using specific primers to amplify p53-RE of the human or mouse Smad6 promoter, or p53-RE in the p21Cip1 promoter as control, were performed and the data were normalized to input chromatin samples of each case and to IgG values=1. Additional control was performed immunoprecipitating with either rabbit IgG or anti-TAp73 and anti-DNp73 specific antibodies, and PCR amplifying the ChIP product with primers specific to a region at the vicinity of the identified p53-RE (1700 bp downstream of the p53-RE), but without homology to this site (H1299 control). Experiments were repeated four times per duplicate. Bars represent mean values±S.E.M; equal variance. Student's t-test was performed to evaluate statistical differences; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001