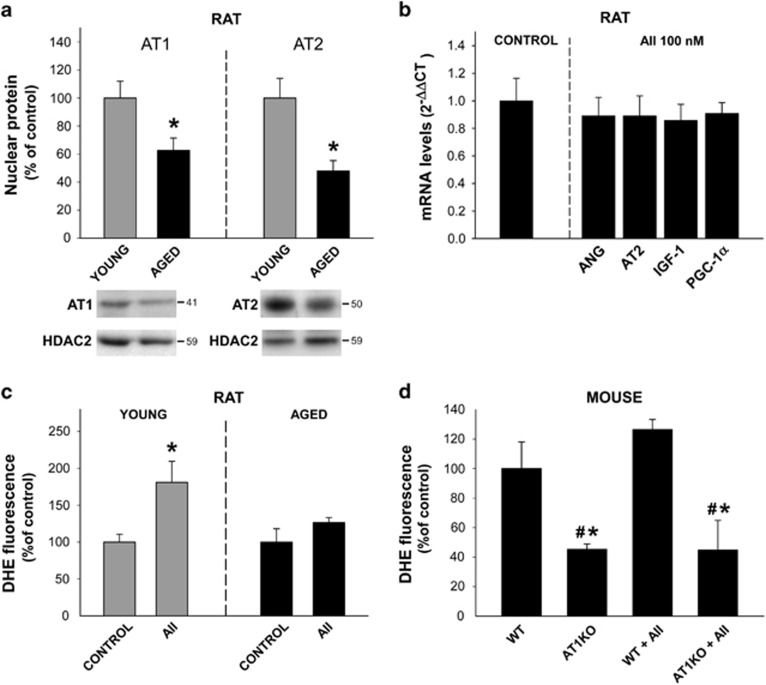
Figure 7.
Nuclear AT1 and AT2 receptors in aged rats and mice. Nuclei isolated from brains of aged rats showed a significant decrease in the levels of both AT1 and AT2 receptors (a). Treatment of nuclei with AII did not induce any significant increase in AT2, angiotensinogen (ANG) and PGC-1α mRNA expression (b), or in the levels of nuclear superoxide/H2O2 (c). Levels of nuclear superoxide/H2O2 were significantly lower in aged KO AT1 mice than in WT aged mice, and treatment with AII did not induce any significant increase in superoxide/H2O2 in nuclei from aged KO AT1 mice (d). Data are mean±S.E.M. *P<0.05 compared to the corresponding control, #P<0.05 compared to aged WT or aged WT treated with AII. One-way analysis of variance and Holm–Sidak post hoc test (b and d) and Student’s t-test (a and c) (n=3–8)