Figure 5.
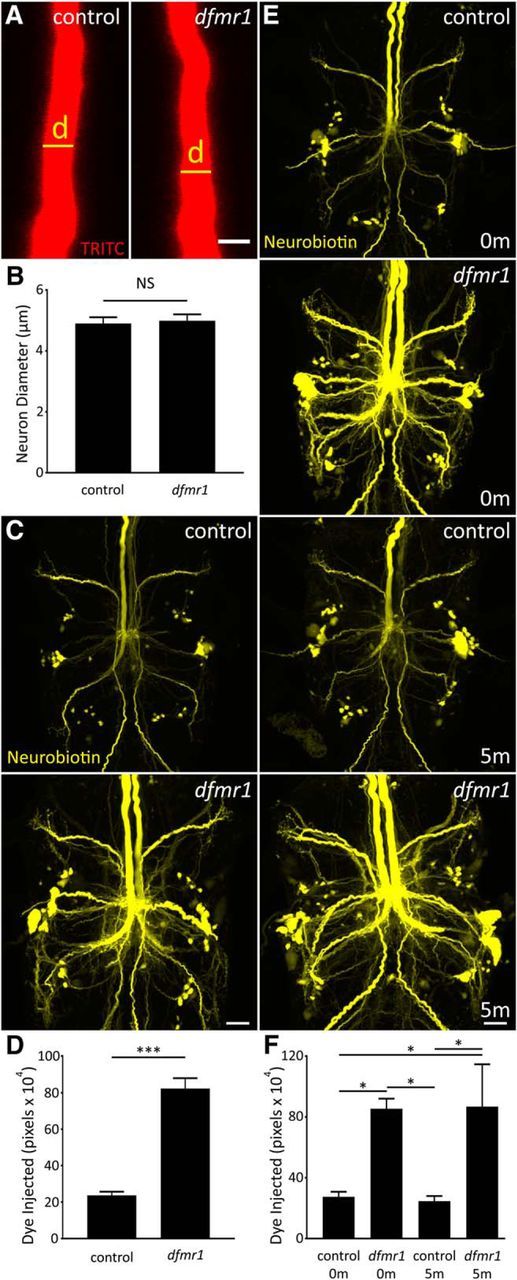
Dye injection defect is not related to multiple GFI neuron properties. A, Representative TRITC injections (ddH2O) showing the GFI descending axon for w1118 genetic background (control; left) and dfmr150M-null mutant (right). Scale bar, 5 μm. B, Quantification of the axon diameter in both genotypes, displayed as the mean ± SEM. Control, n = 15; dfmr1, n = 16. C, Representative NB dye injections into GFI for the w1118 genetic background (control; top) and the dfmr150M-null mutant (bottom) using only KAc-free dye solution (ddH2O). Scale bar, 20 μm. D, Quantification of the injected dye levels, displayed as mean ± SEM. Control, n = 25; dfmr1,n = 26. E, Representative NB injections (ddH2O) into GFI for w1118 genetic background (control; top two panels) and dfmr150M-null mutant (bottom two panels). After dye injection, samples were either immediately dissected (0m) or injected with TRITC for 5 min (5m) with positive current before dissection. Scale bar, 20 μm. F, Quantification of injected dye levels, displayed as the mean ± SEM. 0 m: control, n = 6; dfmr1, n = 6; 5 m: control, n = 6; dfmr1, n = 5. Significance determined from two-tailed unpaired t test (D) and unpaired ANOVA (F): *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001.
