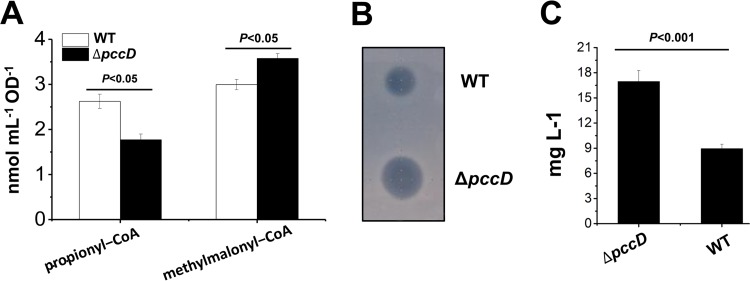
FIG 6.
Apparent increase of erythromycin production in the pccD deletion strain compared to wild type. (A) Intracellular propionyl-CoA and methylmalonyl-CoA concentration of S. erythraea WT and ΔpccD strains grown in TSB medium with 1% (vol/vol) n-propanol. Cells were harvested at 36 h (see Fig. S5B in the supplemental material). (B) Inhibition tests of S. erythraea WT and ΔpccD fermentation broths, collected after culturing for 84 h, against Bacillus subtilis. (C) Erythromycin concentration of S. erythraea WT and ΔpccD strains grown in TSB medium with 1% (vol/vol) n-propanol. Supernatants were collected after culture for 84 h. A turbidimetric method for microbiological assay of antibiotics was used to quantify the erythromycin levels as described in Materials and Methods. Three independent experiments were performed to calculate standard deviation.