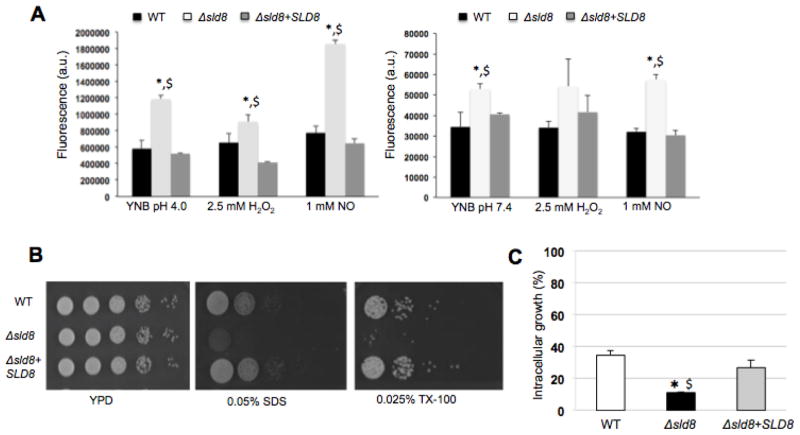
Figure 2. The Δsld8 mutant strain exhibits increased membrane sensitivity and reduced ability to survive inside alveolar macrophages.
A) Fluorescence intensity of Sytox Green after exposing Cryptococcus cells to the dye in acidic (left) or neutral/alkaline pH conditions (right) under oxidative or nitrosative stress (average of three experiments). B) Five microliter spots of serial dilutions starting from 105 cells were placed onto YPD agar plates with or without 0.05% SDS and 0.025% Triton X-100. Plates were incubated at 37 °C in the presence of 5% CO2 and growth monitored (representative images from three experiments). C) Intracellular growth of the wild-type (WT), Δsld8, and Δsld8+SLD8 strains inside primary alveolar macrophages from CBA/J. Two hours post-infection, the cells were washed, fixed with ice-cold methanol, stained with the Giemsa stain for microscopy analysis. A minimum of 100 internalized cryptococcal cells was analyzed for budding to calculate intracellular growth (%). Experiments were performed a minimum of three times and statistical analysis were performed to determine whether changes observed in experiments with the mutant strain were statistically significant compared to the wild-type (shown by *) or the reconstituted strain (shown by $). A p-value of 0.05 was used for all analysis.