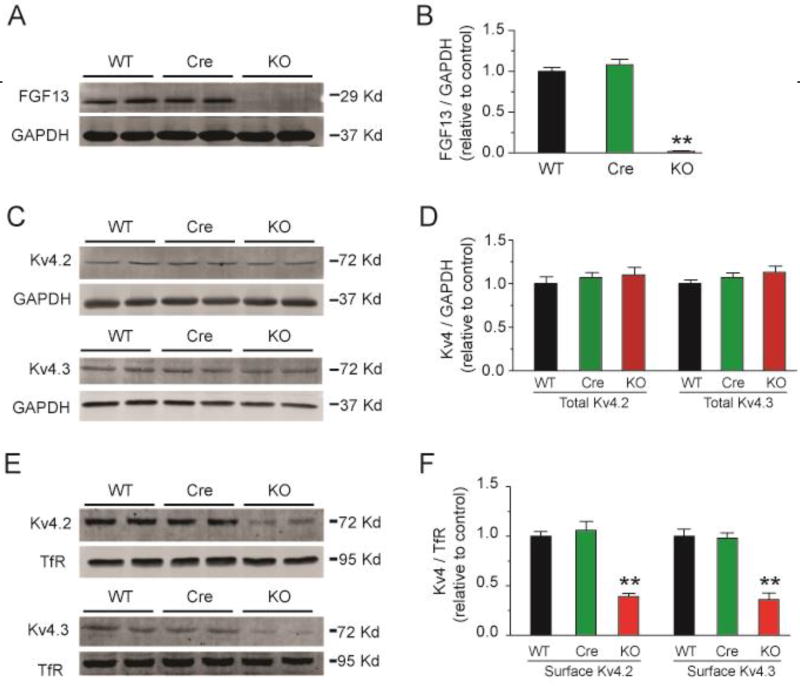
Fig. 7.
Conditional knockout of FGF13 decreases cell surface Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 channels in ventricular cardiomyocytes. (A) Representative immunoblot of FGF13 protein expression in ventricular cardiomyocytes from WT, Myh6-MCM (Cre) and Fgf13 KO (KO) mice. GAPDH was used as loading control. (B) Quantitative analysis of FGF13 protein expression from WT, Cre, and KO mice. ** indicates p<0.01 compared to WT; n=3. (C) Representative immunoblot of total Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 protein expression in ventricular cardiomyocytes from WT, Cre, and KO mice. GAPDH was used as loading control. (D) Quantitative analysis of total Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 protein expression from WT, Cre, and KO mice. n=3. (E) Representative cell surface biotinylaton experiment showing biotinylated Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 protein expression in ventricular cardiomyocytes from WT, Cre, and KO mice. Transferrin receptor (TfR) was used as loading control. (F) Quantitative analysis of cell surface Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 protein expression from WT, Cre, and KO mice. ** indicates p<0.01 compared to WT; n=3.