Figure 1.
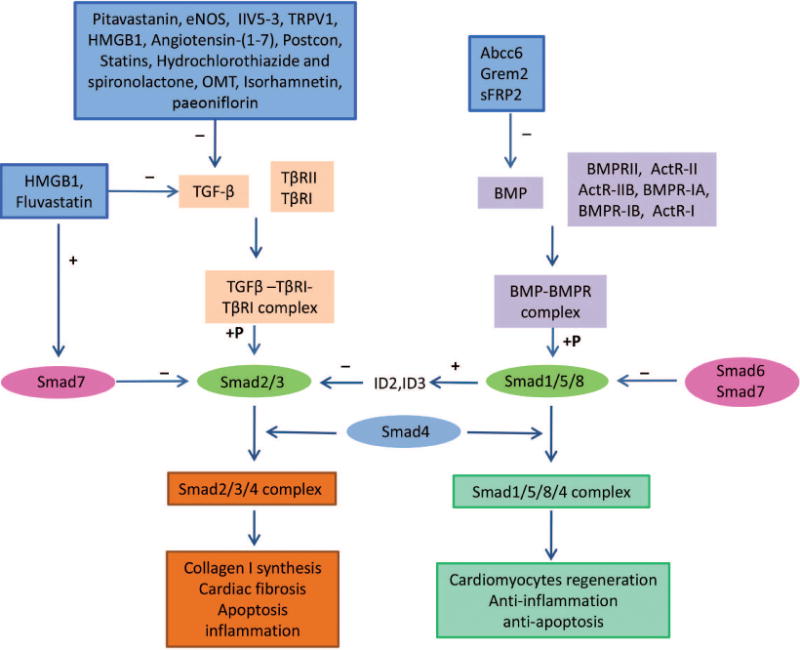
Schematic representation of the role of the TGF-β-Smad and BMP-Smad signaling pathways in myocardial infarction and the mechanisms of some associated potential therapies. Activation of the TGF-β-Smad signaling pathway may be associated with collagen synthesis, cardiac fibrosis, apoptosis, and inflammation. In contrast, activation of the BMP-Smad signaling pathway may be associated with cardiomyocyte regeneration, anti-inflammation, and anti-apoptosis.
