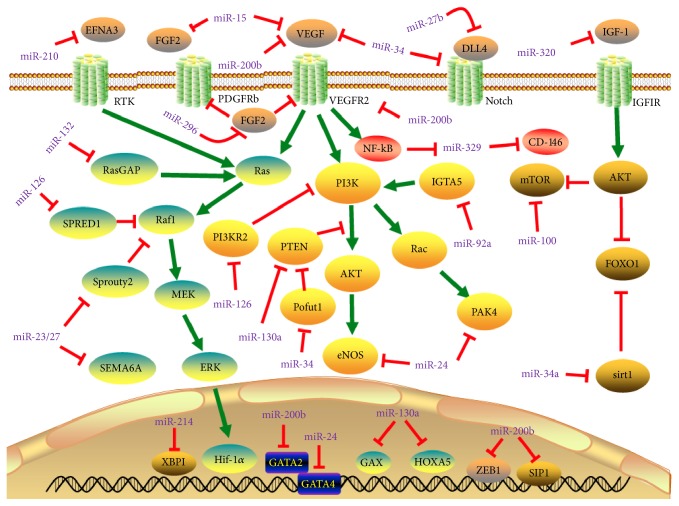
Figure 6.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in angiogenesis pathways. Arrows colored in red indicate the functions of depression; arrows colored in green indicate the functions of activation. Abbreviations for Dll4: delta-like protein 4; Efna3: ephrin A3; eNOS: endothelial nitric oxide synthase; FGF2: fibroblast growth factor 2; Foxo1: Forkhead box O1; GATA2: GATA binding protein 2; Gata4: GATA binding protein 4; GAX: gaseous oxygen; HGS: hepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate; Hif-1α: hypoxia inducible factor 1, α subunit; HOXA5: homeobox A5; IGF-1: insulin-like growth factor 1; IGF-1R: insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; mTOR: mechanistic target of rapamycin; PIK3R2: phosphoinositol-3 kinase regulatory subunit 2; PTEN: phosphatase and tensin homolog; RasGAP: Ras GTPase–activating protein; Sema6A: semaphorin 6A; SIP1: Smad interacting protein 1; SIRT1: Sirtuin 1; Sprouty2: sprouty homolog 2; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR2: vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1; XBP1: X-box binding protein 1; ZEB1: zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 1; RTK: receptor tyrosine kinase; Casp9, caspase 9; Casp3, caspase 3; ERK: extracellular regulated protein kinases; Spread-1: Sprouty-related, EVH1 domain-containing protein 1; PDGFRβ: platelet-derived growth factor receptor β.