Figure 1.
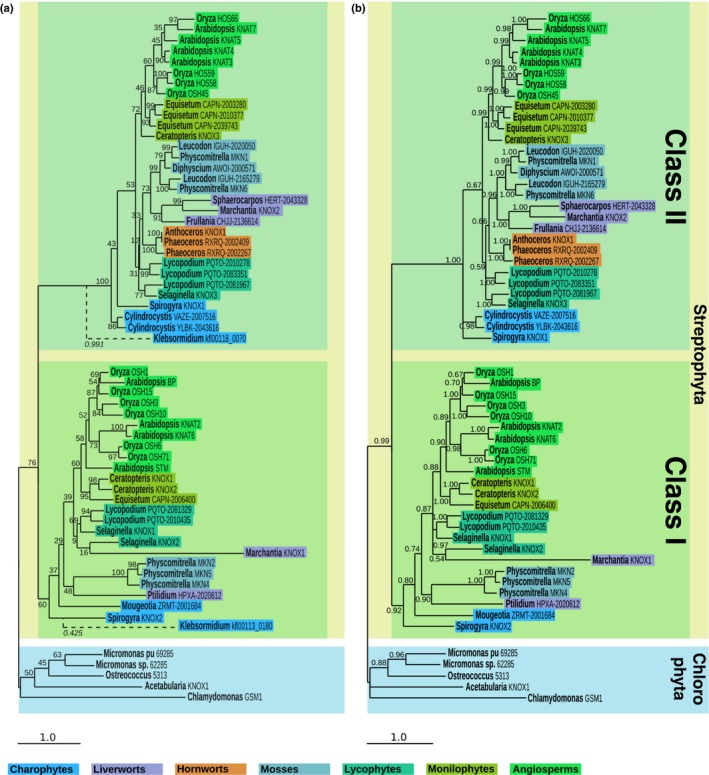
Maximum‐likelihood and Bayesian phylogenetic analysis of KNOTTED‐LIKE HOMEOBOX (KNOX) homologues. (a, b) Phylogenetic trees inferred with (a) RA x ML or (b) MrBayes, using a partitioned nucleotide dataset of 59 + 2 sequences (Supporting Information Fig. S1) evolving under the GTR + Γ + I model. Support values (a, bootstrap values; b, posterior probabilities) are indicated next to the corresponding branch. To avoid destabilization at the base of the Class I clade by Klebsormidium flaccidum sequences, kfl00113_0180 and kfl00118_0070 were added to the maximum‐likelihood tree after the phylogeny was inferred using the evolutionary placement algorithm of RAxML. As a consequence, K. flaccidum sequence branches are dashed and their associated likelihood weight ratios (Stamatakis, 2014) are indicated in italics. Each sequence was placed on its recipient tree branch with respect to the actual distance derived from a maximum likelihood tree inferred using all 61 sequences (Fig. S2). Colour‐coded boxes correspond to the species’ phyla. Both trees were rooted using the Chlorophyta clade as an outgroup.
