Figure 7.
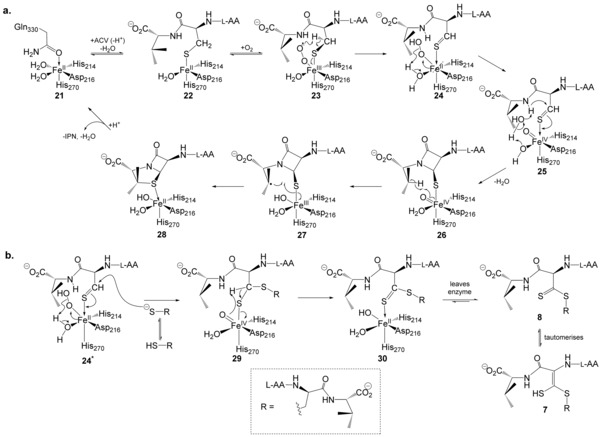
Proposed mechanisms for the reactions of wildtype and I325* IPNS with ACV 1. a) Reaction of wildtype IPNS with ACV (adapted from ref. 25). This scheme shows the “ligand donor” model for peroxide cleavage (24→26), in which the peroxide first reacts with the adjacent water molecule at iron, and the resulting iron‐bound hydroxide then mediates deprotonation of the cysteinyl‐valine amide through a proton shuttle. Recent computational studies20, 21, 48 suggest this route is more likely than alternative “substrate donor” model, in which the peroxide species directly removes the N−H proton of the cysteinyl‐valine amide. b) Proposed mechanism for the conversion of ACV 1 to oxidised product 7 by the I325* mutant, in which the putative thioaldehyde intermediate 24* is intercepted by a second molecule of ACV 1. See the main text for further details of 21–30; l‐AA=l‐δ‐(α‐aminoadipoyl).
