Figure 1.
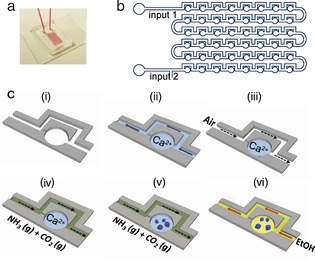
The Crystal Hotel microfluidic device. a) Photograph of a PDMS device bonded to a glass slide and filled with a solution of red dye. b) Chip design of a Crystal Hotel with 48 “rooms”. c) Crystallization in a single room (i). An aqueous solution (light blue) is introduced through inlet 2 to fill the channel and rooms (ii). Subsequently, air (white) is introduced through inlet 1 to push the solution out of the channel and isolate the solution contained in each room (iii). (NH4)2CO3 vapor (green) is then pumped through inlet 1 (iv), and CaCO3 precipitation is initiated by diffusion of CO2 and NH3 gas into the solution (v). Once crystals have formed, ethanol (yellow) is pumped through the device to terminate the reaction (vi).
