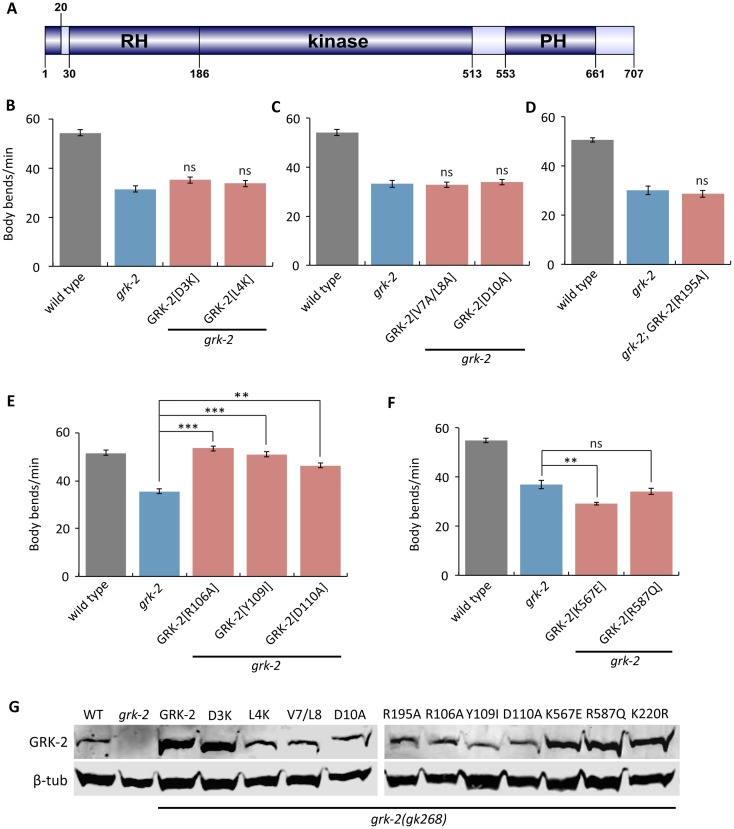
Fig 2. GRK-2 regulation of locomotion requires GPCR-phosphorylation and membrane association.
(A) Domain structure of GRK-2. GRK-2 is a 707 amino acid protein with three well-characterized domains: the RGS homology (RH) domain, the kinase domain, and the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain. The protein structure was drawn using DOG 1.0. (B-D) Residues required for GPCR phosphorylation are required for GRK-2 function in locomotion. The D3K (transgene yakEx77), L4K (transgene yakEx78), V7A/L8A (transgene yakEx79), and D10A (transgene yakEx80) mutations are predicted to block GPCR phosphorylation. The R195A mutation (transgene yakEx95) disrupts predicted intramolecular stabilizing interactions that are required for effective phosphorylation. In each case, expression of the mutant grk-2 cDNA under the control of its own promoter did not rescue the slow locomotion of the grk-2(gk268) mutant (ns, P>0.05, each strain compared to grk-2. Error bars = SEM; n = 10–20). (E) Residues in the RH domain predicted to disrupt Gq binding are not required for GRK-2 function in locomotion. The R106A (transgene yakEx57), Y109I (transgene yakEx55), and D110A (transgene yakEx56) mutations are predicted to disrupt Gq binding. In each case, expression of the mutant grk-2 cDNA under the control of the grk-2 promoter significantly rescued the slow locomotion of the grk-2(gk268) mutant (**, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001. Error bars = SEM; n = 10). (F) Residues in the PH domain predicted to disrupt GRK-2 phospholipid binding or binding to Gβγ are required for GRK-2 function in locomotion. Mutation K567E (transgene yakEx87) is predicted to disrupt GRK-2 phospholipid binding, and mutation R587Q (transgene yakEx88) is predicted to disrupt binding to Gβγ. In both cases, expression of the mutant grk-2 cDNA under the control of the grk-2 promoter did not rescue the slow locomotion of the grk-2(gk268) mutant. (**, P<0.01. ns, P>0.05. Error bars = SEM; n = 10). (G) Verification of the expression of the mutant grk-2 cDNAs used for the experiments shown in Figs 1D and 2B–2F. Western blot analysis of whole worm extracts from grk-2(gk268) mutants expressing the indicated grk-2 mutant cDNAs as extrachromosomal arrays.