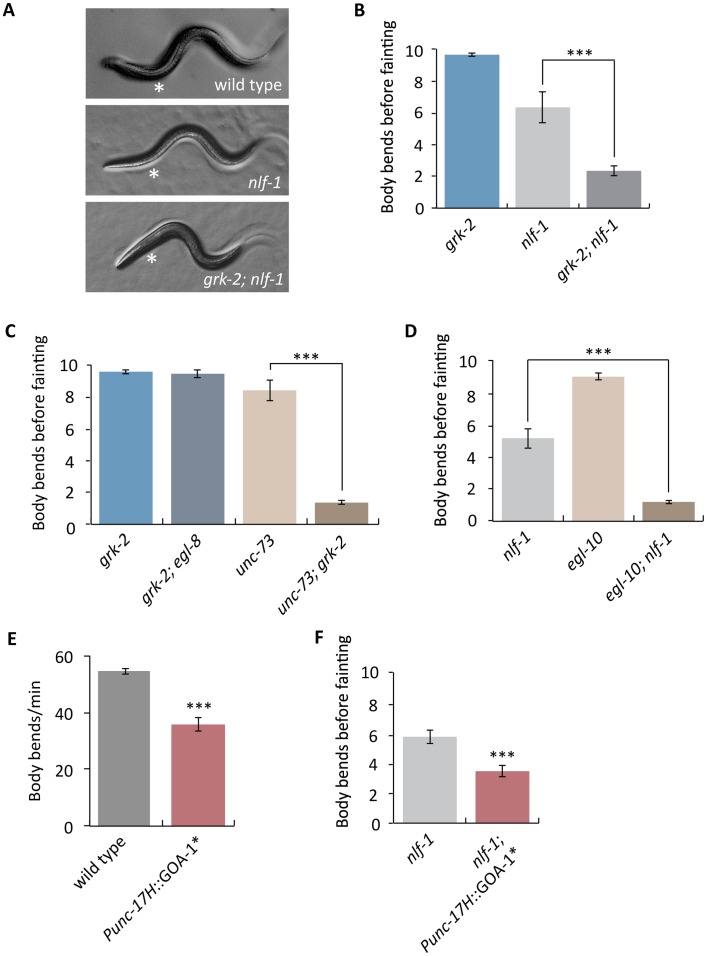
Fig 6. GRK-2 is a positive modulator of NCA-1 and NCA-2 channel activity.
(A) A grk-2 mutation enhances the weak forward fainting phenotype of an nlf-1 mutant. Representative images of wild-type, nlf-1(tm3631), and grk-2(gk268); nlf-1(tm3631) mutant animals. The asterisk shows the anterior part of the worm that becomes straight when an animal faints. (B) A grk-2 mutation enhances the weak forward fainting phenotype of an nlf-1 mutant. The nlf-1(tm3631) mutant is a weak fainter. The grk-2(gk268) mutation enhances the nlf-1 mutant so that the double is a strong fainter. (***, P<0.001. Error bars = SEM; n = 10–20). The number shown is the number of body bends before the animal faints. If the animal made ten body bends without fainting, the assay was stopped and we recorded ten as the number (see Methods). (C) The grk-2(gk268) mutation enhances the unc-73(ox317) mutant so that the double mutant is a strong fainter. The grk-2(gk268) mutation has no effect on an egl-8(sa47) mutant. (***, P<0.001. Error bars = SEM; n = 15). (D) The egl-10(md176) mutation enhances the nlf-1(tm3631) mutant so that the double mutant is a strong fainter. (***, P<0.001. Error bars = SEM; n = 25). (E) Expression of activated Go in head acetylcholine neurons inhibits locomotion. Animals expressing an activated Go mutant (GOA-1[Q205L]) under a head acetylcholine neuron promoter (Punc-17H::GOA-1*, transgene yakEx103) move more slowly than wild-type animals. (***, P<0.001. Error bars = SEM; n = 17). (F) Expression of activated Go in head acetylcholine neurons enhances the weak forward fainting phenotype of an nlf-1 mutant. The nlf-1(tm3631) mutant is a weak fainter in forward movement. The nlf-1(tm3631) mutant expressing an activated Go mutant (GOA-1[Q205L]) under a head acetylcholine neuron promoter (Punc-17H::GOA-1*, transgene yakEx103) is a stronger fainter than the nlf-1(tm3631) mutant. (***, P<0.001. Error bars = SEM; n = 54).