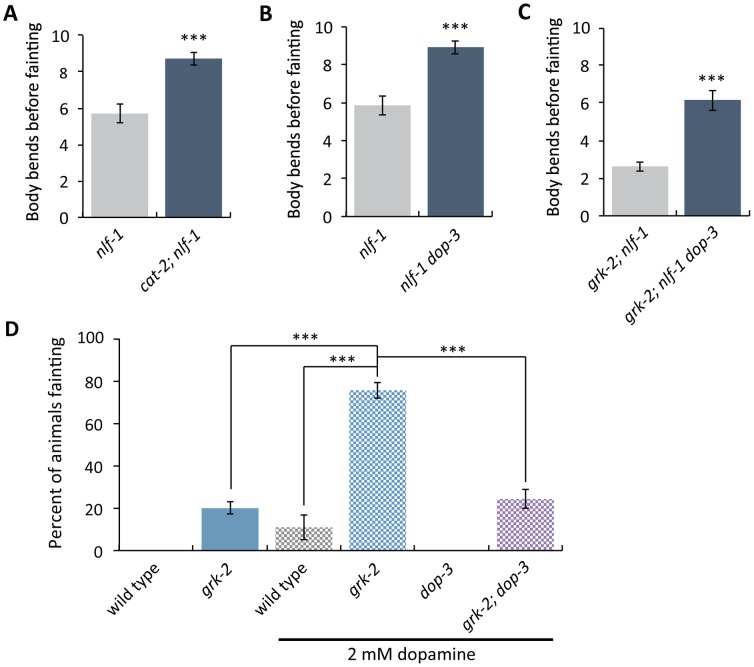
Fig 7. Dopamine negatively modulates NCA-1 and NCA-2 channel activity.
(A) The cat-2(e1112) mutation suppresses the weak forward fainting phenotype of the nlf-1(tm3631) mutant. (***, P<0.001. Error bars = SEM; n = 40). (B) The dop-3(vs106) mutation suppresses the weak forward fainting phenotype of the nlf-1(tm3631) mutant. (***, P<0.001. Error bars = SEM; n = 40). (C) The dop-3(vs106) mutation partially suppresses the strong forward fainting phenotype of the grk-2(gk268); nlf-1(tm3631) double mutant. (***, P<0.001. Error bars = SEM; n = 40). (D) Exogenous dopamine causes the grk-2(gk268) mutant to faint in a dop-3 dependent manner. Shown is the percentage of animals that faint within a period of ten body bends when moving backwards after exposure to 2 mM dopamine for 20 min. (***, P<0.001. Error bars = SEM; n = 2–5 trials of 14–25 animals each).