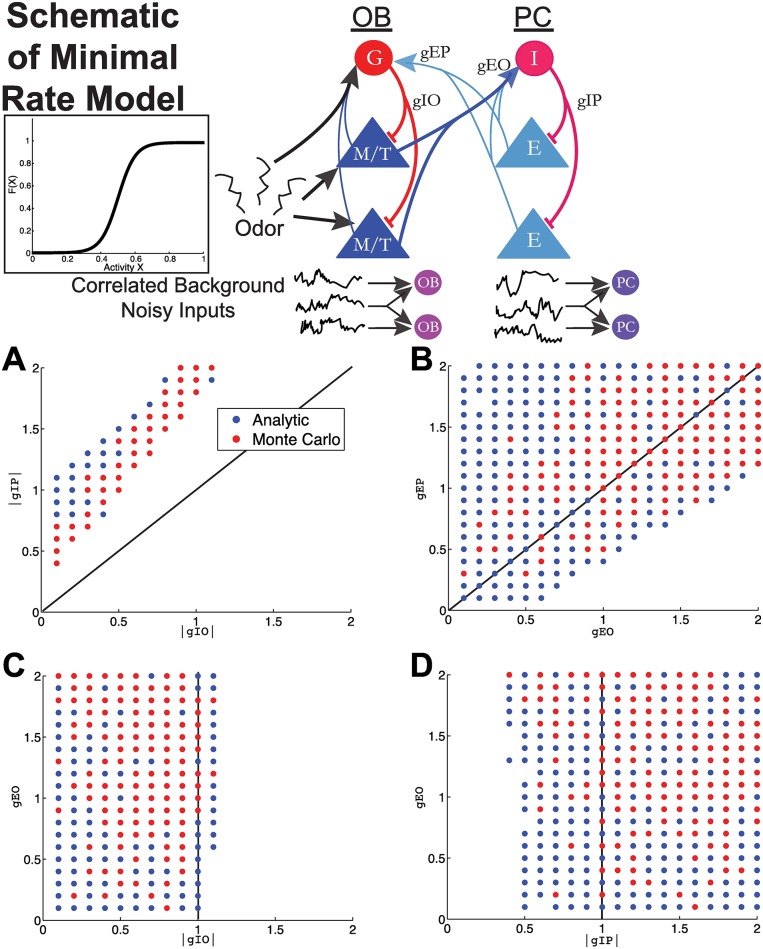
Fig 4. Minimal firing rate model to analyze important synaptic conductance strengths.
A firing rate model (Wilson-Cowan) with background correlated noisy inputs is analyzed to derive principles relating these network attributes (see Eq 1 and Materials and methods section). This model only incorporates some of the anatomical connections that are known to exist and are important for modulation of statistics of firing (see main text for further discussion). Each neuron within a region (OB or PC) receives correlated background noisy input with cOB < cPC. Each plot shows parameter sets (4-tuples) that satisfy all 12 data constraints in Table 1, projected into a two-dimensional plane in parameter space. The blue dots show the result of the fast analytic method that satisfy all constraints; the red dots show the Monte Carlo simulations that satisfy all of the constraints. For computational purposes, we only tested the Monte Carlo on parameter sets that first satisfied the constraints in the fast analytic method. (A) The magnitude of the inhibition within PC (|gIP|) is greater than the magnitude of the inhibition within OB (|gIO|); all dots are above the diagonal line. (B) The excitation from PC to OB (gEP) is generally (but not always) larger than the excitation from OB to PC (gEO). (C) The inhibition within OB is generally weak; dots are to the left of the vertical line. (D) The inhibition within PC is generally strong; dots are to the right of the vertical line. Table 2 shows the parameter values.