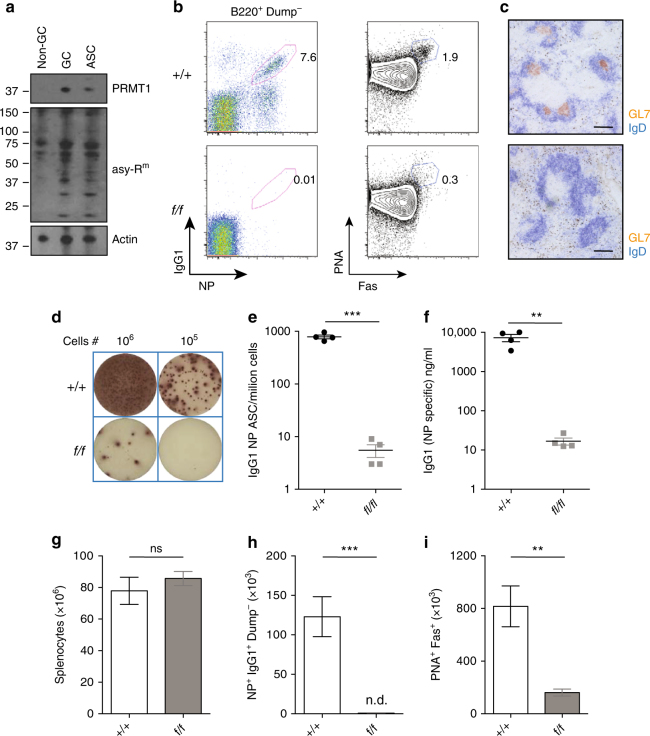
Fig. 4.
PRMT1 is required for GC formation in response to immunization. a Control mice were immunized with NP-KLH in alum and the indicated B-cell subsets were sorted from spleen 7 days post immunization, lysed and proteins separated by SDS-PAGE. Western blot analysis shows PRMT1 (top panel), asymmetrically methylated arginine-containing proteins (middle panel) and actin (loading control, bottom panel) in non-GC B cells (CD19+Fas-PNA−), GC B cells (CD19+Fas+PNA+) and ASC (CD138+B220low). b–i Control (+/+) and Prmt1 f/f CD23Cre (f/f) mice were immunized with NP-KLH in alum and analyzed at day 7. b NP-specific IgG1+ B cells (left) and total GC B cells (right) are shown in representative flow cytometry plots. Numbers indicate frequency of indicated events within the B220+Dump−. Dump antibodies detected IgM; IgD; Gr1. c Immunohistochemical staining for GC in spleen sections at day 7 post NP-KLH immunization using GL7 (orange) and IgD (blue) with scale bars indicating 100 μm. Representative wells d and frequency per million splenocytes e of NP-specific IgG1+ ASC as measured by ELISpot at day 7 post immunization. f Serum titres of NP-specific IgG1 antibody as determined by ELISA at day 7. Total splenocyte number g, number of NP-reactive IgG1+ B cells h and GC B cells (PNA+Fas+) i, calculated at day 7 post immunization of control (+/+) and Prmt1 f/f CD23Cre (f/f) mice as indicated. **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001; ns = not significant (unpaired t-test). Data are representative of three independent experiments with four mice per group. Mean and s.e.m. in e–i. Uncropped images of blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. 5. Flow cytometry gating strategies for this figure are shown in Supplementary Fig. 8