Fig. 7.
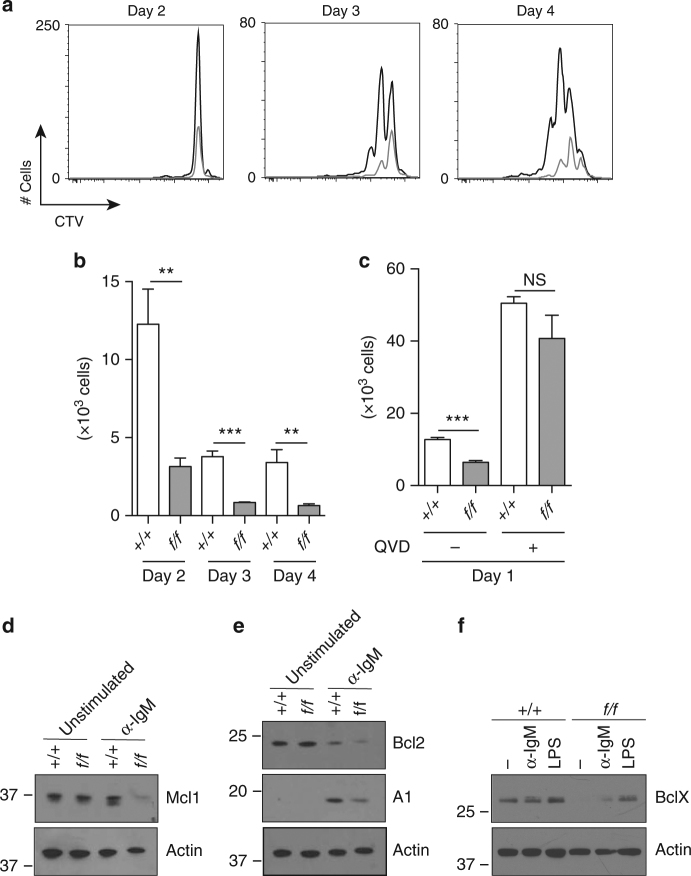
Prmt1-deficient B cells respond abnormally to in vitro stimulation. a, b Splenic B cells, purified from control (+/+) and Prmt1 f/f CD23Cre (f/f) mice, were labelled with CTV and cultured in the presence of F(ab′)2 anti-IgM antibody for the indicated times. a Overlay histograms show division profiles of live cells at days 2, 3 and 4 of activation for control (black line) and Prmt1-deficient (grey line) B cells. b Quantification of live cells at time points indicated after stimulation for control (+/+) and Prmt1-deficient (f/f) samples. c Control (+/+) and Prmt1-deficient B cells (f/f) were activated with F(ab′)2 anti-IgM antibody for 24 h in the presence or absence of the broad caspase inhibitor, QVD. Viable cell numbers are indicated. b, c **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001; ns = not significant (unpaired t-test). Data are representative of three experiments with three replicates per experiment. Mean and s.e.m. d–f Defective regulation of MCL1, BCL2, A1 and BCLX in activated Prmt1-deficient B cells. Immunoblot analysis of spleen B cells from control (+/+) and Prmt1 f/f CD23Cre (f/f) mice. d, e B cells were unstimulated or activated for 24 h with F(ab′)2 anti-IgM, then lysed and separated by SDS-PAGE. d MCL1 and e BCL2 and A1 protein amounts were detected with the respective antibodies. f Control (+/+) and Prmt1 f/f CD23Cre (f/f) spleen B cells were unstimulated (−), activated with F(ab′)2 anti-IgM (α-IgM) or LPS for 24 h, then lysed and separated by SDS-PAGE. BCLX protein was detected by specific antibody as indicated. d–f Actin was used as a loading control and comparable results were obtained in three independent experiments. Uncropped images of blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. 5. Flow cytometry gating strategies for this figure are shown in Supplementary Fig. 11