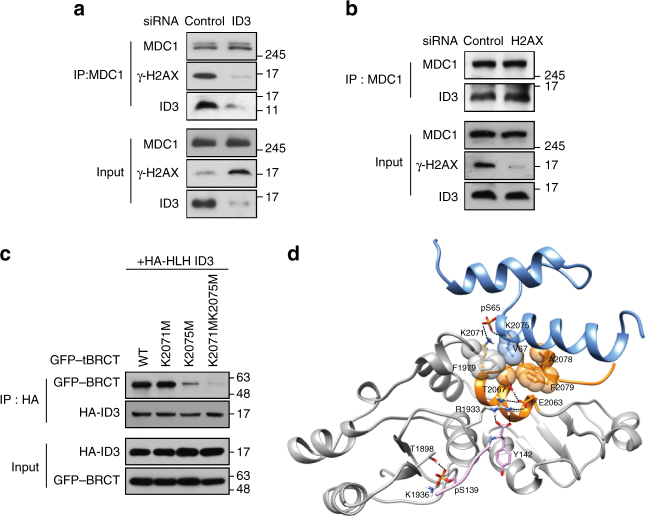
Fig. 6.
ID3 promotes binding of MDC1 to γ-H2AX. a Control and ID3-depleted HeLa cells were treated with and without exposure to IR. 3 h later, whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) using an anti-MDC1 antibody, and western blotting using anti-MDC1, anti-γ-H2AX and anti-ID3 antibodies as indicated to the right of the blot. b Control and H2AX-depleted HeLa cells were treated with and without exposure to IR. After 3 h, whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation using an anti-MDC1 antibody, and western blotting using anti-MDC1, anti-γ-H2AX, and anti-ID3 antibodies as indicated to the right of the blot. c GFP-tagged versions of each of the tBRCT point mutants were expressed in HEK293T cells together with the HLH domain of ID3. About 3 h after irradiation, cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation and western blotting using antibodies as indicated to the right of the blot. d A model of the three-dimensional protein structures for the proposed trimer of MDC1–tBRCT, γ-H2AX, and ID3-pHLH is shown. The blue ribbon represents phosphorylated ID3-HLH, the gray ribbon represents the tBRCT domain of MDC1, the orange ribbon represents the region of tBRCT where ID3 binds, and the pink ribbon represents the γ-H2AX pentapeptide. Relevant amino acid residues are numbered, and notable hydrogen bonding is indicated by a black dashed line. Uncropped blots of this Figure accompanied by the location of molecular weight markers are shown in Supplementary Fig. 14