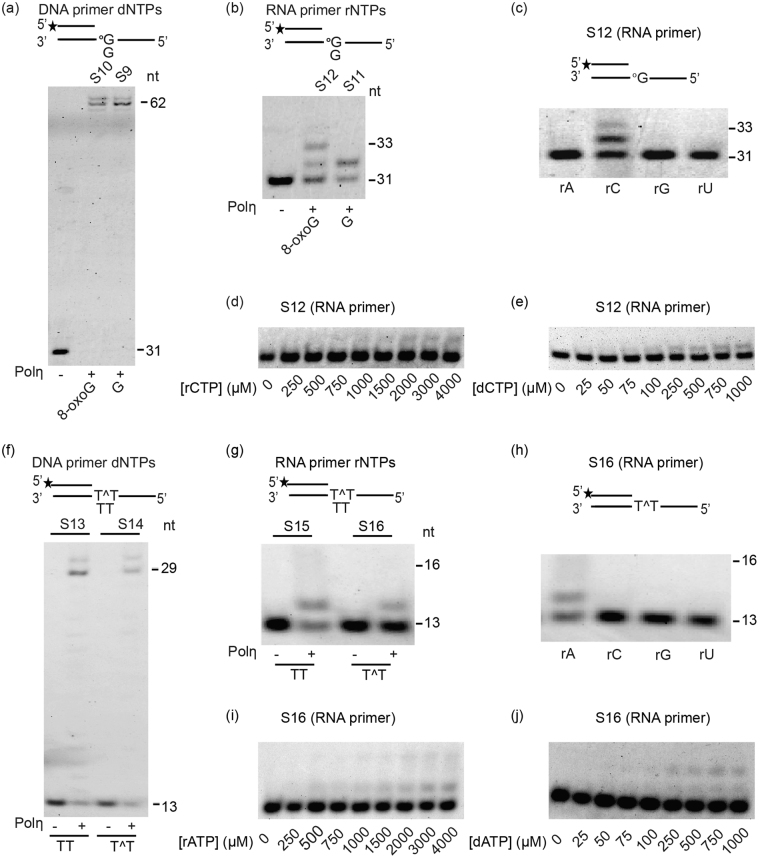
Figure 4.
Polη can carry out error-free bypass of 8-oxoG and TT dimer during RNA extension. (a) Polη (56 nM) can synthesize through a G, and an 8-oxoG containing template (8 nM both) during DNA extension with dNTPs (100 µM) and (b) also during RNA extension with rNTPs (100 µM) (c) Polη (10 nM) inserts only the correct C (4 mM of each rNTP) opposite 8-oxoG (8 nM). (d) Kinetic assay for rCTP and (e) dCTP insertion opposite 8-oxoG. (f) Polη (18 nM) can synthesize through an undamaged TT and a TT dimer containing template (16 nM both) during DNA extension with dNTPs (100 µM), as well as (g) during RNA extension with rNTPs (1 mM). (h) Polη (18 nM) inserts only the correct A (4 mM of each rNTP) opposite a TT dimer (16 nM). (i) Kinetic assay of rATP and (j) dATP insertion opposite a TT dimer. In reactions shown in (d,e) 1 nM Polη was incubated with 8 nM template. In (i,j) reactions contained 1 nM Polη and 16 nM template. Conditions for the kinetic assays of (d,e,i,j) are detailed in Materials and Methods. The positions of the normal G or 8-oxoG (°G), and the two Ts or the TT dimer (TΛT) in the substrates are indicated Asterisks mark the 5′ Cy3 labeled ends. See Fig. S5 for full-length images.