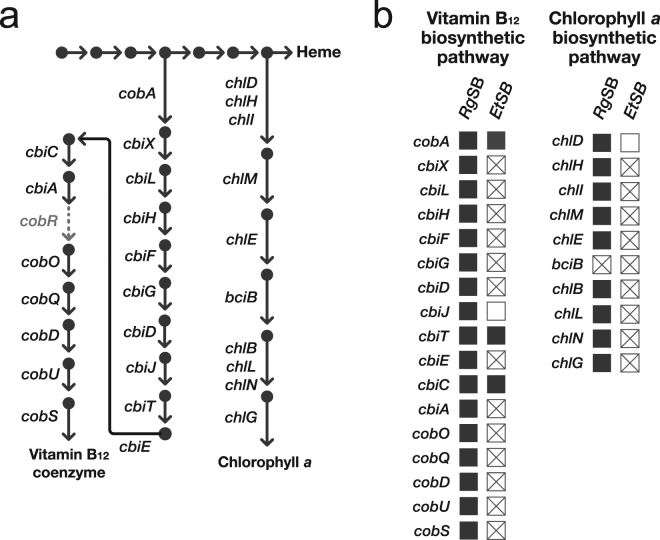
Figure 2.
Chlorophyll a and vitamin B12 biosynthetic pathways in the spheroid bodies of Rhopalodia gibberula (RgSB) and Epithemia turgida (EtSB). (a) Pathways for chlorophyll a and vitamin B12 biosynthesis. Each arrow indicates a single reaction. Gene names corresponding to each reaction are displayed. The step indicated by a dashed grey arrow is catalysed by cobyrinic acid a,c-diamide reductase (encoded by cobR) in diverse photosynthetic organisms, but this gene was not detected in the genome of the RgSB, EtSB, or their close free-living relatives (i.e. Cyanothece spp.). (b) Status of genes for the chlorophyll a and vitamin B12 biosynthetic pathways in the RgSB and EtSB genomes. A filled box indicates the presence of an intact gene, whereas a box with a X mark and a blank box designate the presence of a pseudogene and the absence of a gene, respectively.