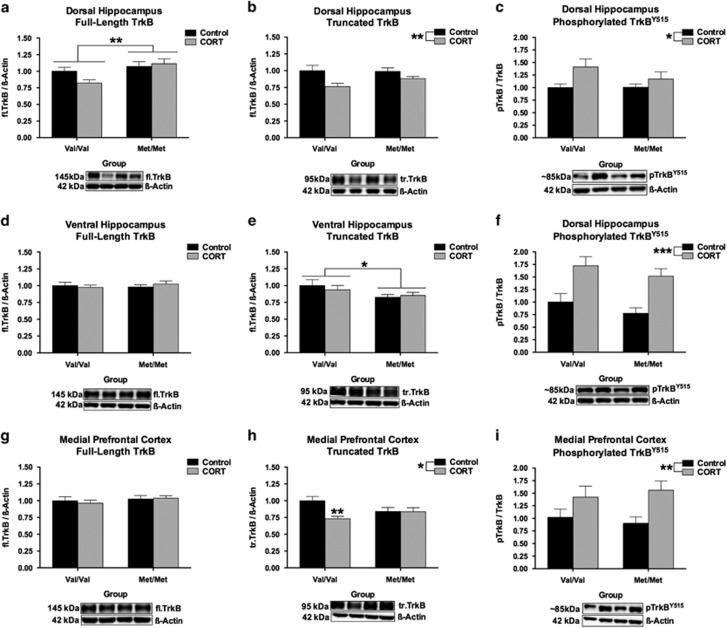
Figure 4.
Effects of hBDNFVal66Met genotype and prior CORT exposure on TrkB isoforms. (a) hBDNFMet/Met mice have (subtly) higher fl.TrkB expression relative to hBDNFVal/Val mice in the DHP, while chronic CORT tends to (b) decrease tr.TrkB expression while (c) increasing TrkBY515 phosphorylation in this brain region. In the VHP, (d) fl.TrkB was unchanged however (e) hBDNFMet/Met mice tended to have lower tr.TrkB expression than hBDNFVal/Val mice. (f) CORT treatment increased pTrkBY515 phosphorylation in the VHP. In the mPFC, (g) fl.TrkB was once more unchanged. (h) However, a significant genotype × treatment interaction emerged for tr.TrkB expression whereby hBDNFVal/Val mice selectively responded to chronic CORT. Following CORT, expression levels of tr.TrkB in the mPFC of hBDNFVal/Val mice were reminiscent of those observed in the mPFC of hBDNFMet/Met mice. (i) Lastly, as in the DHP and VHP, a history of CORT also increased pTrkBY515 phosphorylation in the mPFC. All data presented as mean±SEM; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001. Per group, n=9–14.