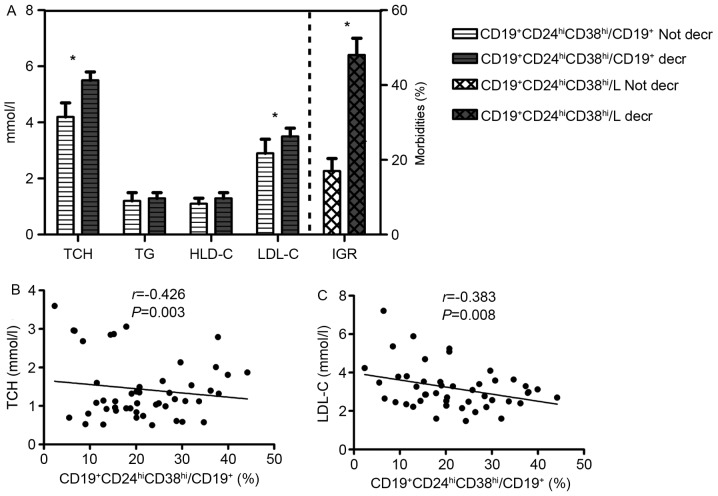
Figure 3.
Clinical implication of CD19+CD24hiCD38hi Bregs in patients with HT. (A) The decrease in ratio of CD19+CD24hiCD38hi Bregs to lymphocytes (CD19+CD24hiCD38hi/L) significantly increases the morbidity associated with DM; HT patients with decreased CD19+CD24hiCD38hi/L (n=20) had significantly higher levels of TCH and LDL-C, compared with those without (n=64). The decrease in the ratio of CD19+CD24hiCD38hi Bregs to CD19+ lymphocytes (CD19+CD24hiCD38hi/CD19+) was associated with high (B) TCH and (C) LDL-C levels. *P<0.05 vs. Not decr. Data is presented as mean ± standard deviation. Bregs, regulatory B cells; HT, Hashimoto's thyroiditis; CD19+CD24hiCD38hi/L, ratio of CD19+CD24hiCD38hi Bregs to lymphocytes; DM, diabetes mellitus; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; IGR, impaired glucose regulation; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TCH, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride.