Figure 3.
Development and Validation of an HCS Assay to Detect Tau Levels in i3Neurons
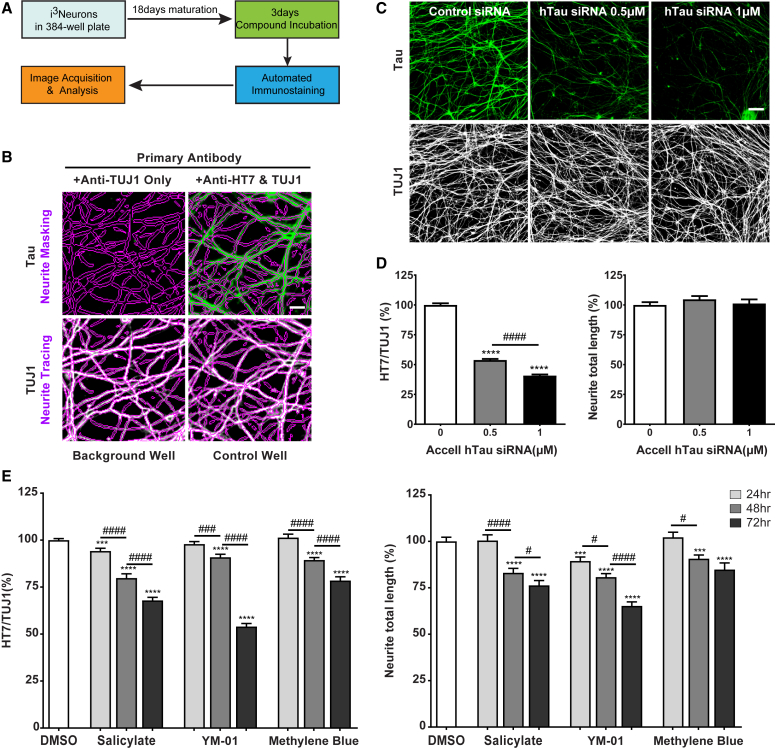
(A) Schematic of the HCS assay optimized to measure cellular tau levels in neurons treated with small-molecule compounds.
(B) Representative fluorescence high-content images showing tau (green) and βIII tubulin (white) channels from a background well (left, anti-TUJ1 only) and a control well (right, anti-HT7 and TUJ1). Neurite regions (purple) were traced according to the TUJ1 channel and were applied to the tau channel with the neuronal profiling module of Cellomics software. Scale bar, 10 μm.
(C) Representative fluorescence high-content images showing tau (green) and βIII tubulin (white) channels from i3Neurons after 7 days of treatment with control siRNA or human tau siRNA (0.5 or 1 μM). Scale bar, 50 μm.
(D) Automated quantification of human tau levels (left) and neurite total length (right) from i3Neurons treated with human tau siRNA. Data are from three independent experiments, total N = 42 per treatment; values are means ± SEM relative to control siRNA. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 compared with control siRNA, STATA mixed model. ####p < 0.0001, STATA mixed model.
(E) Automated quantification of human tau levels (left) and neurite total length (right) from i3Neurons treated with 5 mM salicylate, 1 μM YM-01, or 1.5 μM methylene blue for 24–72 hr. Data are from three independent experiments, total N = 42 per treatment; values are means ± SEM relative to DMSO. ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, compared with DMSO, STATA mixed model; #p < 0.05, ###p < 0.001, ####p < 0.0001, comparison between three time points within each compound treatment, STATA mixed model.
See also Figure S3.