Figure 21.
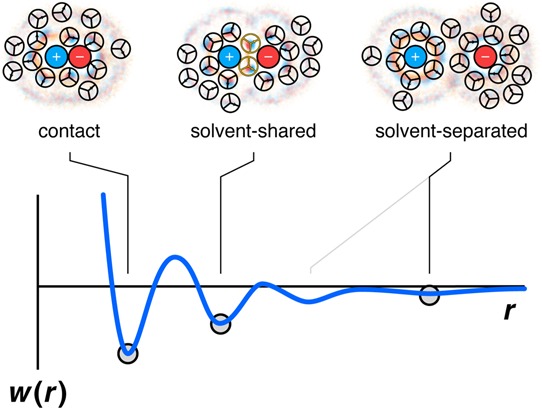
The water structure around an ion pair depends on the cation–anion distance. At large separations, each ion has its own solvation shell. At intermediate separations, the ion pair is stabilized by bridging waters. Ion–ion contacts of opposite charge are stabilized by electrostatic attractions, in addition to the water forces. (blue) Positive charge density of the waters. (red) Negative charge density of the waters. (orange) Density of the water–water hydrogen bonding arms.
