Fig. 2.
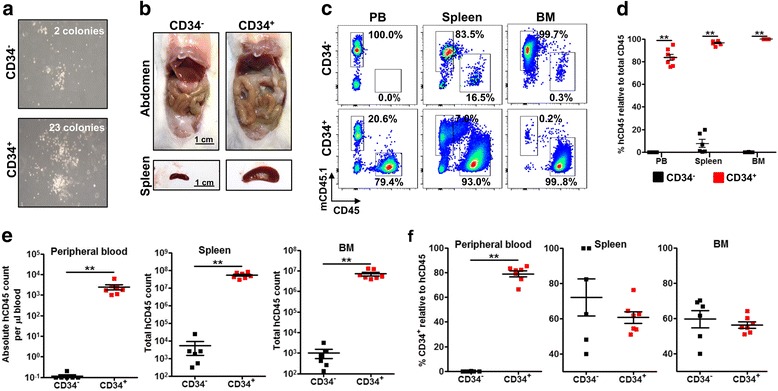
CD34+ AML cells have greater proliferative and engraftment capacity than CD34− AML cells. Pooled BM cells and splenocytes from Leu 14 primary engrafted mice were FACs-sorted to CD34+ and CD34− fractions. a Methocult™ colony-forming unit (CFU) assay of CD34+ and CD34− cells. Representative images at 3 weeks post-culture were shown. Colonies were counted microscopically, and the mean number of colonies obtained in duplicate dishes (1 × 103 cells inoculated per dish) was indicated. b Evaluation of pathological outcome at week 10 post-engraftment. Representative images of abdomen and spleen from CD34+ or CD34− engrafted mice (5 × 105 cell injected per pup) were shown; scale bar: 1 cm. c The level of AML engraftment in peripheral blood, spleen, and BM. Representative flow cytometry plots illustrating the frequency of mouse CD45.1+ cells and human CD45+ cells from CD34+ cells (n = 7) or CD34− cells (n = 6) engrafted mice were shown. d, e Comparison of AML engraftment in peripheral blood, spleen, and BM between CD34+ and CD34− cells engrafted mice at endpoint. Data are presented as mean frequency (d) or absolute count (e) of human CD45+ cells ± SEM. Two-tailed Mann Whitney U test; **p < 0.01. f Comparison of frequency of total CD34+ cells relative to human CD45 cells in peripheral blood, spleen, and BM between CD34+ and CD34− cells engrafted mice at endpoint. Data are presented as mean frequencies ± SEM. Two-tailed Mann Whitney U test; **p < 0.01
