Figure 4.
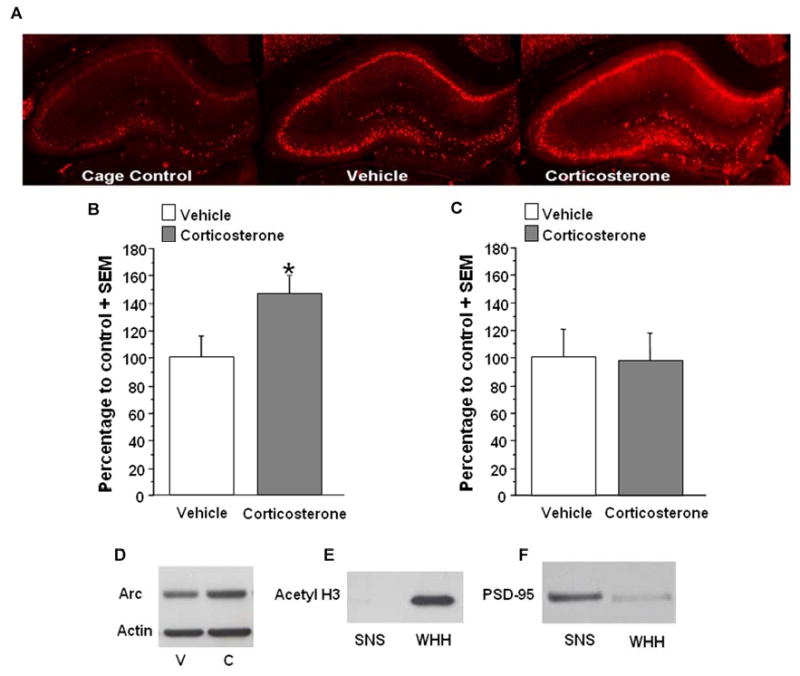
A. Immunohistochemical analysis of the effect of systemic corticosterone on Arc protein in the hippocampus of animals trained on an inhibitory avoidance task. Memory-enhancing injections of corticosterone (3 mg/kg, i.p.) appear to increase Arc immunoreactivity in the dorsal hippocampus, particularly in the dendrites of the CA1 region and dentate gyrus. B. Western blot quantification of corticosterone effect on Arc protein expression in synaptoneurosome fractions of the hippocampus. In animals trained on an inhibitory avoidance task, memory-enhancing injections of corticosterone (3 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly increase Arc expression in synaptoneurosome fractions (corticosterone, n=8; vehicle, n=7; *p<.05) C. Corticosterone treatment (3 mg/kg) did not significantly affect Arc protein expression in synaptoneurosome fractions (corticosterone, n=8; vehicle, n=7) taken from animals that were not trained. D. Western blot from synaptoneurosome fractions of rats receiving either vehicle (V) or corticosterone (C) injections. E. Western blot for acetyl H3. Acetyl H3 is present in the whole hippocampal homogenate (WHH) but not in synaptoneurosome fractions (SNS). F. Western blot for PSD-95. There is a 5-fold enrichment of PSD-95 in synaptoneurosome (SNS) fractions compared to whole hippocampal homogenate (WHH). Densitometry values for Arc are normalized to actin and to cage control and then presented as a percentage of the control vehicle group. Data are presented as mean + SEM.
