Fig. 3.
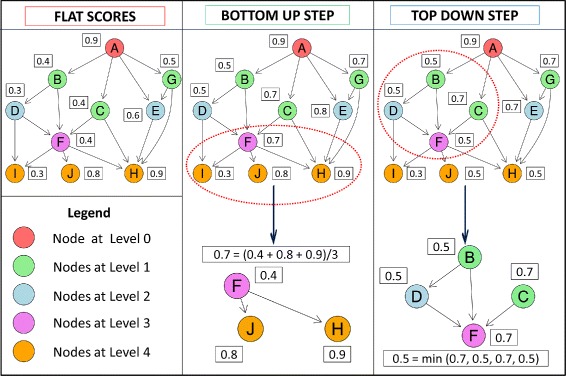
A toy example of the operating mode of the TPR-DAG method. Left: The nodes represent different HPO terms and the numeric values the flat scores associated to each node of the graph. The different colors represent the levels, i.e. the maximum distance of the node from the root node A. Center: The bottom-up step introduces a correction of the flat scores by taking into account the scores of the children of each node. This procedure is methodically repeated from the bottom to the top nodes of the DAG; as an example, the bottom part shows that the correction for the F node is performed by averaging the flat score of the F parent node with those of the “positive” children, i.e. that children nodes having a value larger than that of the F parent node. Right: The Top-down step introduces a further correction by taking into account the scores of the parent nodes, by methodically parsing this time the DAG from the root node A down to descendant nodes; as an example, the bottom part of the figure shows that the score of the F node is set to the minimum of the bottom-up scores of F and that of its parents A, B and C
