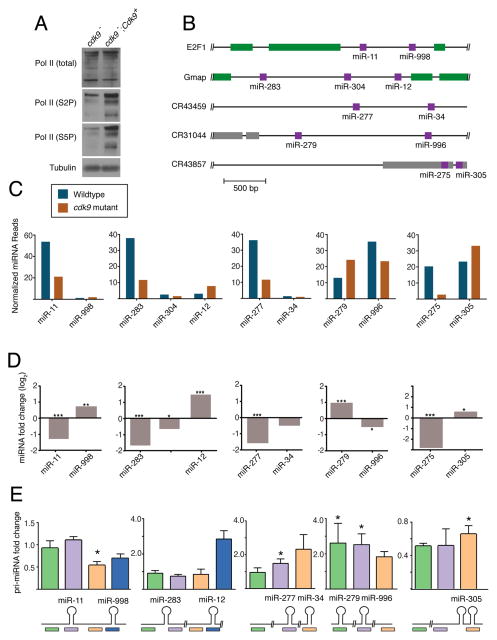
Figure 4. Cdk9 is required for differential miRNA processing.
See also Figure S2. (A) Western blot of total Pol II and specific phospho-isoforms of Pol II from cdk9 mutant tissue. (B) Schematic structures of five polycistronic genes that were analyzed for miRNA expression. (C) Levels of mature miRNAs expressed from polycistronic genes. Shown are normalized RNA-seq read levels (1000s) from animals that are wildtype and cdk9 mutant. (D) Differential expression of mature miRNAs between mutant and wildtype animals as determined by RNA-seq. (*, p ≤ .01; **, p ≤ .001; ***, p ≤ .0001; edgeR exact test). (E) Differential expression of pri-miRNAs between mutant and wildtype animals as determined by RT-qPCR. Shown below are positions of the various RT-qPCR products being assayed. Error bars are standard deviations. (*, p ≤ .01; t-test)