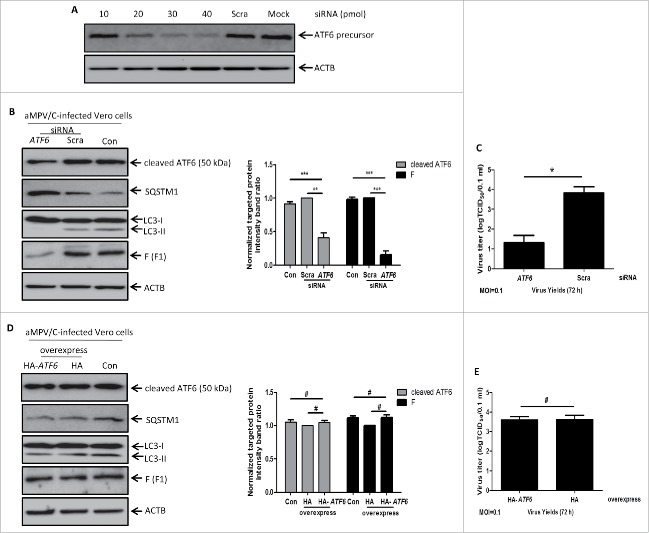
Figure 6.
Knockdown of the endogenous ATF6 gene inhibits aMPV/C-induced autophagy and virus production. (A) Vero cells were mock-transfected (mock) or transfected with ATF6-siRNA at different concentrations (10, 20, 30 or 40 pmol), or 40 pmol scrambled-siRNA (Scra). ATF6 protein was detected by western blotting at 48 h. (B) Vero cells were transfected with ATF6-siRNA, Scra and Con (siRNA-untransfected) and then infected with aMPV/C for 72 h. The cells were harvested and analyzed by western blotting with anti-ATF6, anti-SQSTM1, anti-LC3, anti-viral F, and anti-ACTB antibodies. Representative results are displayed with graphs corresponding to the ratios of ATF6:ACTB or viral F:ACTB normalized to the control conditions. (C) Vero cells were transfected and infected as described in B. Progeny virus yields were examined by TCID50 at 72 hpi in Vero cells. (D) Vero cells were transfected with pCMV-HA (HA) or pCMV-HA-ATF6 (HA-ATF6) plasmid and then infected with aMPV/C for 72 h. The cells were harvested and analyzed by western blotting with anti-ATF6, anti-SQSTM1, anti-LC3, anti-viral F, and anti-ACTB antibodies. Representative results are displayed with graphs corresponding to the ratios of ATF6:ACTB or viral F:ACTB normalized to the control conditions. (E) Vero cells were transfected and infected as described in D. Progeny virus yields were examined by TCID50 at 72 hpi in Vero cells. Error bars, mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments. Two-way ANOVA test, #P > 0.05; *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001, compared with the control group.