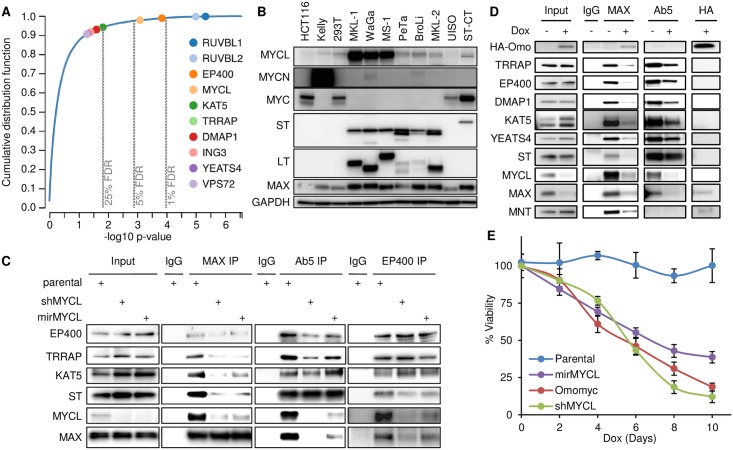
Fig 3. ST requires MYCL to sustain MCC viability.
(A) CRISPR-Cas9 screen of MKL-1 cells was analyzed in the MAGeCK-VISPR pipeline. Cumulative distribution function of p-values plotted based on 18,493 human genes. EP400 complex components and MYCL were identified in CRISPR screen negative selection with p-values < 0.05 were indicated. See also S3A–S3C Fig and S2 Table. (B) Lysates from virus-positive MCC cell lines MKL-1, WaGa, MS-1, PeTa, BroLi and MKL-2, virus-negative MCC cell line UISO, and additional lines were immunoblotted. ST-CT are UISO cells stably expressing C-terminal epitope tagged ST. (C) Lysates from MKL-1 cell lines containing Dox-inducible shRNA (shMYCL) or miRNA (mirMYCL) specific for MYCL, prepared 2 days after addition of 0.3 μg/ml Dox (Input), were immunoprecipitated for MAX, Ab5, EP400 or non-specific IgG and blotted. (D) MKL-1 cells containing Dox-inducible HA tagged Omomyc before (-) or after (+) 5 days of Dox treatment. Dox (0.3 μg/ml) was added every two days. Lysates (Input) were immunoprecipitated with non-specific IgG, MAX, Ab5 and HA antibodies and blotted. (E) Viability of MKL-1 Dox-inducible cell lines described in C and D. 3,000 cells of each line were aliquoted in 96 well plate on day 0. Total days of Dox treatment is indicated on the X axis. Fresh medium or medium with 0.3 μg/ml Dox was supplemented every two days. At the end of time course (day 10), all samples were assessed for viability by CellTiter-Glo (Promega). Values were normalized to untreated samples of each inducible cell line. Three biological replicas were performed. Data are presented as mean (SD).