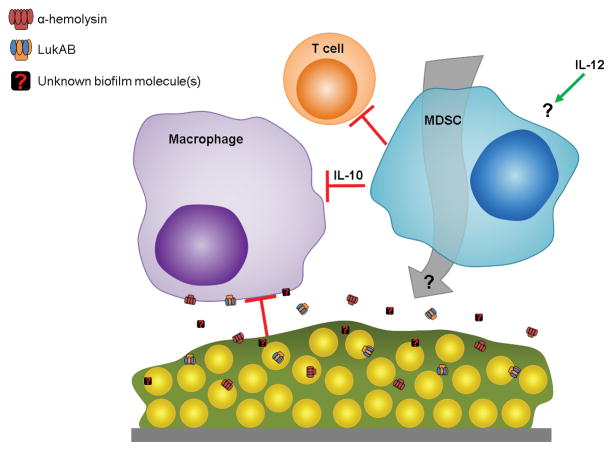
Figure 1. Model for S. aureus biofilm immune evasion.
Toxins secreted from S. aureus biofilms, including α-toxin (Hla) and LukAB, inhibit macrophage microbicidal function and induce cell death. Additional unidentified molecules released from staphylococcal biofilms, either via active secretion or following bacterial cell lysis, likely contribute to maximize inhibition of host antimicrobial activity. MDSC recruitment by a yet unknown mechanism(s) that requires IL-12 suppresses T cell activity and induces a local anti-inflammatory milieu characterized by IL-10 production. Biofilm-mediated immune polarization results in biofilm persistence and chronic disease.