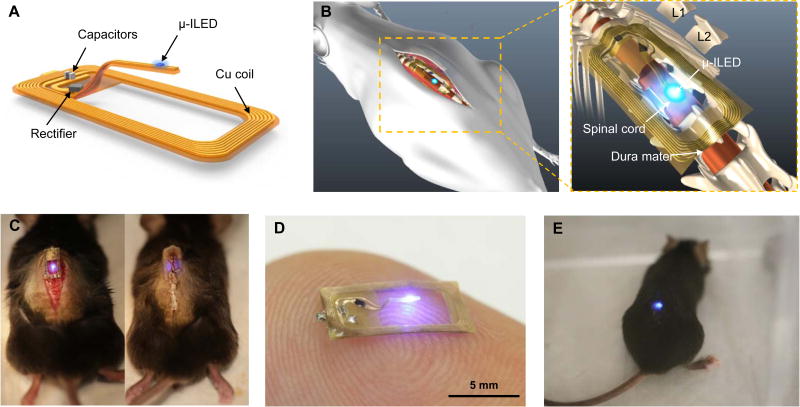
Figure 1. Overall design of the flexible wireless optoelectronic system and the anatomy of the system on the spinal cord.
(A) Schematic illustration of the overall system design with open architecture and µ-ILED positioned at the end of the probe stem. (B) Diagram demonstrating the anatomy and location of the optoelectronic system as implanted above the spinal cord. (C) Images of intermittent steps during implantation of the optoelectronic system in the mouse before (left) and after (right) the implantation. (D) Representative image of a device in the ‘ON’ state while resting atop an index finger. (E) Representative image of an awake, freely moving mouse with the optoelectronic system implanted on the spinal cord.