Fig 1.
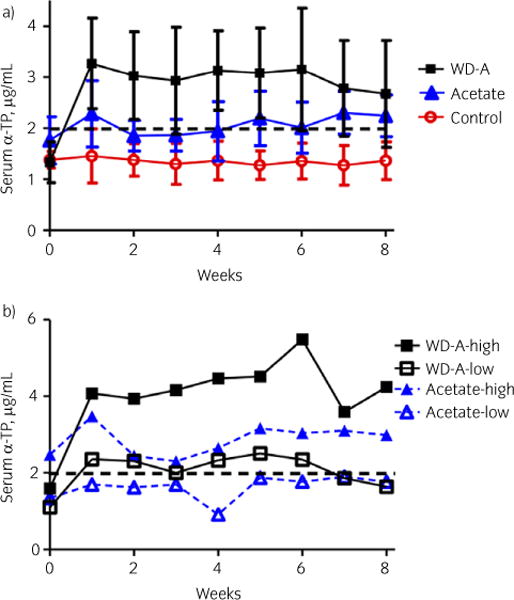
a) Mean ± s.d. serum α-tocopherol (α-TP) concentrations in control horses receiving no supplemental α-TP, horses receiving 5000 IU/day of RRR-α-TP acetate and horses receiving 5000 IU/day of water-dispersible (WD) RRR-α-TP for 3 weeks, followed by a tapering dose of WD RRR-α-TP and increasing dose of RRR-α-TP acetate, culminating in 5000 IU RRR-α-TP acetate for the final week. b) Serum concentrations of α-TP in the horse with the highest and horse with the lowest responses to acetate and combination α-TP supplementation. There was inter-individual variation in response to supplementation. The dotted line indicates the lower limit of the normal range [22].
