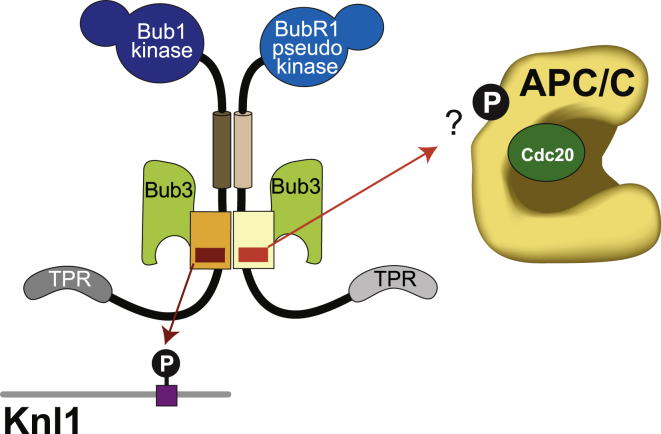
Figure 7.
Model for the Differential Functions of the BubR1 and Bub1 Loop
Model showing the different functions of the loops in BubR1 and Bub1. Bub1 and BubR1 form a pseudo-symmetric heterodimer through the B3BDs and the helix as well as through the presence of Bub3. The loops are not involved in this interaction but serve different functions. The Bub1 loop enhances binding of the Bub1:Bub3 complex to Knl1-MELTP motifs, which in turn recruits BubR1:Bub3 to kinetochores. The BubR1 loop, however, is not able to enhance such an interaction of Bub3 with Knl1 but instead seems to promote binding of BubR1:Bub3 to the APC/C. This is required for the SAC function of BubR1. We hypothesize that this interaction could work via modulation of Bub3 and be regulated in a phosphorylation-dependent manner, arguing that the BubR1 loop functions in analogy to the Bub1 loop.