Figure 7.
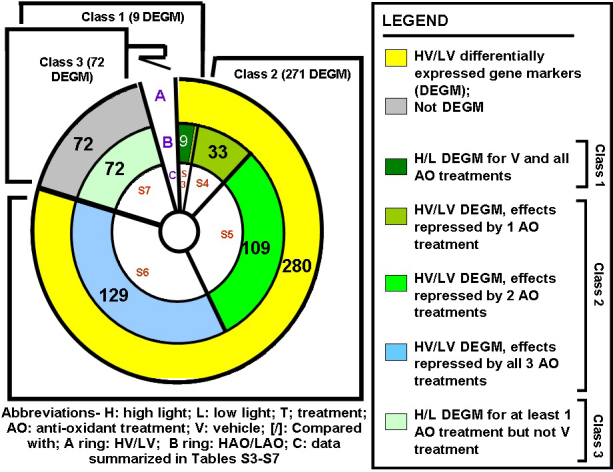
Three classes of induced gene markers. The (H/L) differential gene expression data across all four dietary treatments (352 gene markers) was partitioned into vehicle effects (A ring, HV/LV) and antioxidant (AO) effects (B ring, HAO/LAO); 280 of these gene markers define light (the transition from a low to high light rearing environment) responses. Nine gene markers with a similar fold change expression trend in all four analyses define class 1 genes (Appendix 7) that correspond to high light effects that cannot be inhibited with antioxidant treatment; 271 HV/LV differentially expressed gene markers where the differential phenotype is inhibited by at least one of the antioxidant treatments define class 2 genes (light effects that can be modified by an antioxidant treatment; Appendix 8, Appendix 9, Appendix 10 and Appendix 11); and 72 class 3 genes are characterized by a HAO/LAO differential status in at least one of the antioxidant treatments but not for HV/LV, thus defining purely antioxidant effects in a high light environment (Appendix 11).
